* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1: Matter and Energy HW Packet
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Liquid–liquid extraction wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Sol–gel process wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
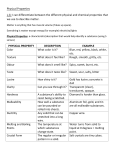
Name: ___________________________________ Period: __________ Date: ____________ Unit 1: Matter and Energy HW Packet Part 1: Classify each of the following as a PURE SUBSTANCE or a MIXTURE. 1. Sucrose ____________________ 5. Concrete ____________________ 2. Hot Tea ____________________ 6. Vinegar ____________________ 3. Table Salt ____________________ 7. Helium ____________________ 4. Motor Oil ____________________ 8. Water ____________________ Part 2: Classify each of the following Mixtures as either HOMOGENEOUS or HETEROGENEOUS. 1. Oxygen Dissolved in Water _________________ 5. Gasoline ____________________ 2. Carbon Mixed with Sand _________________ 6. Coca Cola ____________________ 3. Filtered Apple Juice _________________ 7. Chunky Peanut Butter __________________ 4. Freshly Squeezed Lemonade _________________ 8. Italian Dressing ____________________ Part 3: Classify each of the following Pure Substances as either ELEMENTS or COMPOUNDS. 1. Water ____________________ 4. Oxygen ____________________ 2. Table Salt ____________________ 5. Alcohol ____________________ 3. Mercury ____________________ 6. Platinum ____________________ Part 4: Write the chemical symbol for each of the following elements. 1. Lithium ____________________ 4. Chlorine ____________________ 2. Phosphorus ____________________ 5. Sulfur ____________________ 3. Sodium ____________________ 6. Potassium ____________________ Part 5: Name the chemical elements represented by the following symbols. 1. Cu ____________________ 4. F ____________________ 2. H ____________________ 5. N ____________________ 3. Ag ____________________ 6. Au ____________________ Part 6: Complete the chart below: Compound NH4Cl KMnO4 KI CHCl3 C3H7OH # of Elements # of Atoms Part 7: Classify these samples of matter as one of the following: PURE SUBSTANCE – ELEMENT MIXTURE – HOMOGENEOUS PURE SUBSTANCE – COMPOUND MIXTURE – HETEROGENEOUS 1. Water and Oil: ____________________ 8. Granite: ____________________ 2. Salt Water: ____________________ 9. Gold: ____________________ 3. Paint: ____________________ 10. Apple: ____________________ 4. Sodium Chloride: ____________________ 11. Water and Sand: ____________________ 5. Black Ink: ____________________ 12. Leather: ____________________ 6. Plutonium: ____________________ 13. Air: ____________________ 7. Shaving Cream: ____________________ 14. Carbon Dioxide: ____________________ Complete the Hierarchy of Matter Schematic with the Classification of Matter titles. Spaghetti sauce Glass (SiO2) Muddy Water Iron Water (H2O) Corn Oil Orange Juice Silver Table Salt (NaCl) Apple Oxygen Black Coffee Isopropyl Alcohol (C3H7OH) Mint Chocolate Chip Ice Cream ______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ Part 8: Decide whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. 1. __________ Both elements and compounds are pure substances. 2. __________ A heterogeneous substance has at least two pure substances in it. 3. __________ Pure substances have variable composition. 4. __________ Compounds have variable composition while elements do not. 5. __________ A compound must contain at least 2 elements. 6. __________ Homogeneous mixtures exist in one phase. 7. __________ Homogeneous mixtures cannot be separated. 8. __________ All elements are represented by a chemical formula. Part 9: Label each of the following properties as either PHYSICAL or CHEMICAL. 1. combustibility _________________ 7. density ____________________ 2. malleability _________________ 8. volume ____________________ 3. weight _________________ 9. melting point ____________________ 4. failure to react _________________ 10. flammability ____________________ 5. ductility _________________ 11. odor ____________________ 6. texture _________________ 12. tendency to corrode___________________ Part 10: Classify each of the following changes as either PHYSICAL or CHEMICAL. 1. digestion of food ____________________8. exploding fireworks ____________________ 2. getting a haircut ____________________9. lighting a candle ____________________ 3. boiling water ____________________10. tarnishing silver ____________________ 4. melting butter ____________________11. forming acid rain ____________________ 5. crushing rocks ____________________12. dissolving salt ____________________ 6. burning gasoline ____________________13. the sun drying dew ____________________ 7. slicing bread ____________________14. shattering glass ____________________ Part 11: Classify each of the following physical properties as EXTENSIVE or INTENSIVE. 1. density ____________________ 6. melting point ____________________ 2. color ____________________ 7. length ____________________ 3. mass ____________________ 8. hardness ____________________ 4. texture ____________________ 9. volume ____________________ 5. shape ____________________ 10. boiling point ____________________ Part 12: Refer to the illustrations below to answer the following questions about VISCOSITY. A B C D E A B C D 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Figure 1 Figure 2 In Figure 1, which test tube contains the liquid with the highest viscosity? __________ In Figure 1, which test tube contains the liquid with the lowest viscosity? __________ In Figure 2, which test tube contains the liquid with the highest viscosity? __________ In Figure 2, which test tube contains the liquid with the lowest viscosity? __________ What would happen if the liquids in Figure 1 were heated? ___________________________________ What do you know about the falling rate of the marbles in Figure 2 if the liquids in Figure 2 are cooled? ___________________________________________________________________________________ Part 13: Density Show the correct location of the following items in a density column. (Draw a graduated cylinder.) Water = 1.0 g/mL Aluminum = 2.67 g/mL Motor Oil = 0.91 g/mL Balsa Wood = 0.4 g/mL Corn Syrup = 2.34 g/mL Use the graph below to answer the following questions about DENSITY. 1. 2. 3. 4. What is the volume of this substance if the mass is 300 g? ____________________ Using the mass and volume from question #1, what is the density of the substance? _______________ Now that you know the density of the substance, identify the substance. ____________________ Is the density of a substance an extensive or intensive property? ____________________ Use the graph below to answer the following questions about DENSITY. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. If the mass is 50 grams, the volume is __________ cm3. If the mass is 100 grams, the volume is __________ cm3. If the mass is 250 grams, the volume is __________ cm3. What is the density of the material shown on this graph? _________________ If this substance were place in water, would the substance sink or float? _______________ Part 14: Match each term with the correct definition. 1. __________ Chemical Reaction a. matter is not created or destroyed in a chemical reaction 2. __________ Reactants b. starting substances in a chemical reaction (on the left) 3. __________ Products c. ability of a substance to undergo chemical reactions 4. __________ Chemical Property d. absorbs heat from the surroundings 5. __________ Exothermic Reaction e. releases heat to the surroundings 6. __________ Endothermic Reaction f. substances produced in a chemical reaction (on the right) 7. __________ Law of Conservation g. process in which one or more substances change into Of Mass new substances Part 15: Complete the following short answer section. 1. When 400 grams of wood are burned, 30 grams of ash remain. The law of conservation of mass states that you cannot destroy matter, so what happened to the missing 370 grams of matter? __________________________________________________________________________________ 2. The following changes happen to a sample of gasoline. Tell if each is a chemical change or a physical change and give a reason for your choice. a. Gasoline boils ______________________________________________________ b. Lead is added to gasoline ______________________________________________________ c. Gasoline burns ______________________________________________________ d. Gasoline is poured in a tank ______________________________________________________ 3. 16 grams of methane gas combine with 64 grams of oxygen to form 44 grams of carbon dioxide, plus water. What mass of water is produced? 4. In an engine, octane combines with oxygen gas to form carbon dioxide and water. If 22.8 grams of octane react with 80 grams of oxygen gas, 70.4 grams of carbon dioxide is produced, plus water. What mass of water is produced? 5. When 127g of copper reacts with 32 grams of oxygen gas to form CuO. How much copper (II) oxide is produced? 6. According to the law of conservation of mass, how much zinc was present in the zinc carbonate? 7. Refer to the picture which shows ice melting. a. Is this a physical change or a chemical change? b. What do you know about the temperature inside the ice? c. What do you know about the temperature around the ice? d. Is this an endothermic or exothermic process? 8. Refer to the picture which shows paper burning. a. Is this a physical change or a chemical change? b. Is this an endothermic or exothermic reaction? Part 16: Match the following types of energy with the correct description. 1. __________ Chemical a. energy of motion 2. __________ Electrical b. stored energy or energy due to position 3. __________ Electromagnetic c. energy stored in chemical bonds between atoms 4. __________ Kinetic d. energy that travels as waves 5. __________ Potential e. electron movement 6. __________ Thermal f. total energy of particles (heat) Part 17: Fill in the blank to correctly complete each statement. 1. _______________ properties can be observed without chemically changing matter. 2. _______________ properties describe how a substance reacts with other substances. 3. _______________ have definite shapes and definite volumes. 4. _______________ have a definite volume but are able to change shape. 5. _______________ can change their shape and volume. 6. Phase changes are always _______________ changes. 7. _______________ is the phase change where a solid changes to a liquid. 8. _______________ is the phase change where a liquid changes to a solid. 9. The _______________ and freezing points for a substance are equal. 10. _______________ is the phase change where a liquid changes to a gas. 11. _______________ is the phase change where a gas changes to a liquid. 12. The _______________ and condensation points for a substance are equal. 13. _______________ is the phase change where a solid changes directly to a gas without turning to a liquid first. 14. _______________ is the resistance to flow by a fluid (liquid or gas). 15. Substances that are very thick and gooey have a _______________ viscosity. 16. Substances that are very runny have a _______________ viscosity. 17. When substances are heated, their viscosities _______________. 18. When substances are cooled, their viscosities _______________.