* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide - Issaquah Connect
Survey
Document related concepts
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
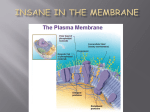
t I NHnrc SECTION 3.3 t)ntc Porlo<l CELL MEMBRANE Study Guide c) g v, -c¡Ã13 C KEY CONCEPT VOCABULARY The cell membrane is a barrier that separates a cell from the external environment. cell membrane selective permea bility phospholipid receptor ciT => ol rri áÐ .rt (¡l c fluid mosaic model CI =L o = MAIN IDEA: Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. 1. Draw a phospholipid in the box below. Label the three major parts. Phosphate group; glycerol; fatty acid co>o, E Which part of a phospholipid is charged or polar? the charqed 3. V/hich part of a phospholipid is nonpolar? the fattv acid tails 4. What type of molecules interact with water, polar or nonpolar? 5. Where does a cell membrane come into contact with water? 6. Why do rhe phospholipids surrounding the cell form o .S =co phosphate and qlycerol 2. a polar outside the cell bilayer? the polar headsinteract with water E o) f o f q) : A cell membrane has other types of molecules embedded in the phospholipid bilayer, List function of each type of molecule in the table below a o o) l o oo o E 'E o o t) Molecule Function 7. Cholesterol strengthen the cell membrane 8. Proteins nerp malenars cross rne memprane, pan oT cyrosKerelon 9. Carbohydrates Unit 2 Besource Book McDougal Littell Biology nerp toenilry ceil types Study Guide I I)atc Pcriocl Narne STUDY GUIDE, CONTINUED o (J cã 1O. In what way is a membrane fluid? ThephospholipidsineachlayercanmoVefromsidetosi@ 6â lJ- r¡¡ rLe= <= 11. Draw a picture in the box below to represent selective permeability (J= inside outs¡de P CN o) (J Refer to figure 3.18 for visual awnser MAIN !DEA: Chemical signals are transmitted across the cell membrane. 12. A receptor detects a signal molecule and carries out an action in response. f3. A is a molecule that acts as a signal when it binds to a receptor. ligand 14. A ligand that can cross the cell membrane can bind to an intracellular receptor t C 15. A ligand a that cannot cross the cell membrane can send a message to a cell by binding to membrane o o E o receptor, which then chanqes C) shape. .c Vocabulary Gheck 16. What is the fluid mosaic model? the fluid mosaic model is a description of the arrangement of the molecules that make up a cell mem o 17. The cell membrane allows some, but not all, molecules to cross. What term describes this property? ) o) ôo o selective permeability c o) o o O 10 Study Guide Unit 2 Resource Book McDougal Lìttell Biology