* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
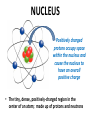
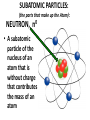
Describing the Structure of ATOMS MATTER • Anything that has volume and mass • Everything that exists is matter, and is made of ATOMS ATOM • The smallest unit of an element that has all of the properties of that element containing a nucleus within an electron cloud. MODEL OF THE ATOM • A conceptual model of the atom showing a small positively-charged nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons, much like the planets orbit the Sun in our Solar System. NUCLEUS Positively charged protons occupy space within the nucleus and cause the nucleus to have an overall positive charge • The tiny, dense, positively-charged region in the center of an atom; made up of protons and neutrons ELECTRON CLOUD Negatively charged electrons occupy the space within the electron cloud and cause the electron cloud to have an overall negative charge • All of the area of an atom, outside the nucleus where electrons are found SUBATOMIC PARTICLES (the parts that make up the Atom): PROTON, p+ • A positivelycharged subatomic particle of the nucleus of an atom that contributes to the mass of the atom SUBATOMIC PARTICLES: (the parts that make up the Atom): 0 NEUTRON, n • A subatomic particle of the nucleus of an atom that is without charge that contributes to the mass of an atom SUBATOMIC PARTICLES: (the parts that make up the Atom): ELECTRON, e • A negatively-charged subatomic particle of the electron cloud that is involved in the formation of chemical bonds ELECTRICAL CHARGE Each electron has a negative charge Each proton has a positive charge Neutrons are without charge • A form of charge, designated negative, positive, or neutral (has no charge) that is found on the subatomic particles that make up all atoms.