* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Livermorium wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Particle-size distribution wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
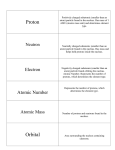
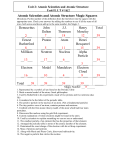
The Periodic Table: Elements and Compounds Vocabulary Periodic table: A chart in which elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties. atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number of protons in the nucleus is the atomic number, which determines the identity of an element.) neutron: a subatomic particle that has no charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. electron: a subatomic particle that has a negative charge. element: a substance that cannot be separated or broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. compound: a substance made up of atoms of two ore more different elements joined by chemical bonds. atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. (The atomic number is the same for all atoms of an element.) chemical symbol: a one, two, or three-letter abbreviation of the name of an element on the periodic table. Molecule: A particle made up of two or more atoms bonded together. Metal: An element that is typically a hard, shiny solid, is malleable, and is a good conductor of heat and electricity Metalloid: An element that shares some properties of metals and some of nonmetals Nonmetal: An element that is usually a gas or brittle solid at room temperature, is not malleable or ductile, is a poor conductor of heat and electricity, and is typically not shiny