* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Golgi Apparatus 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
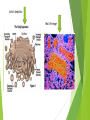
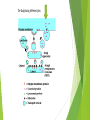
Golgi Apparatus By Kirsten Lydon What is a Golgi apparatus? Sometimes called a Golgi body A flattened stack of membranes that form a complex structure Individual stacks are called cisternae Latin for “collecting vessels” Cisternae vary in number 1 to a few in protists 20 or more in animal cells Several hundred in plant cells Artist’s depiction Real life image What does it do? Functions include the collection, packaging, distribution, and modification of molecules These molecules are synthesized in one location of the cell and are used in another. Some may leave the cell through the cellular membrane Like the mailroom of the cell A vesicle transporting proteins out of the cell What does it do? (cont.) Proteins and lipids made on the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER) are modified as they pass through the Golgi apparatus ex. The addition or modification of short sugar chains which make: Glycoproteins and glycolipids It also synthesizes cell wall components Noncellulose polysaccharides that form the cell wall of plants are synthesized in the Golgi body. Afterwards, they are sent to the plasma membrane and are added to cellulose which assembles the exterior of the cell. The Golgi doing different jobs It has a front and back The front is called the cis face Usually found near the ER Materials enter the Golgi body in transport vesicles that come from the ER Lumen Cavity where proteins, to be secreted by the cell, are packaged in vesicles to be released The back is called the trans face Materials are discharged from this face in secretory vesicles Lysosomes Come from the Golgi apparatus Contain a high level of degrading enzymes How does it move materials? It is proposed that material moves through the cell by means of: cisternal maturation Transport of vesicles between cisternae And direct tubular connections The primary accepted method of transport is cisternal maturation When individual cisternae mature from early cis to late trans Because the cisternae are so tightly stacked together it is hard to give a definitive answer as to how transport actually occurs. Protein transport through endomembrane system Connected to Alzheimer's disease It is an irreversible, progressive brain disease that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills. Causes dementia and eventually death In Alzheimer’s disease, the Golgi bodies seem to fall apart or become fragmented as it progresses.