* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration Overview
Survey
Document related concepts
Mitochondrial replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
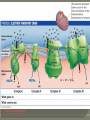
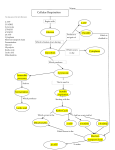
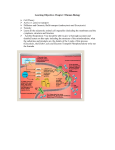
The process in which organisms take molecules broken down from food and release the chemical energy stored in the chemical bonds of those molecules • Remember, food is NOT the direct source of energy! Heterotrophs Only and Autotrophs Autotrophs undergo PHOTOSYNTHESIS Goal: break down glucose to form two pyruvates Who: ALL life on Earth performs Glycolysis Where: The Cytoplasm Glycolysis produces 4 ATP’s and 2 NADH • Uses 2 ATP’s in the process for a NET of 2 ATP’s and 2 NADH Goal: Take Pyruvate and produce NADH & FADH2 Where: The inner mitochondrial matrix Net yield: • • • • 8 NADH 2 FADH2 2 ATP 6 CO2 Goal: Break down NADH and FADH2 by pumping H+ into the outer compartment of the mitochondria Where: The mitochondria A gradient is created to produce ATP • Electrons continue down the energy gradient until they meet the ultimate electron acceptor (Oxygen!) Produces 32 ATP • ATP is generated as H+ moves down its concentration gradient through a special enzyme called ATP Synthase Cellular Respiration C6H12O6 What + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O do you notice about this equation? Have you seen bits of it before?? Working in small groups (2-3) complete the Case Study on my website Answer the Questions at the end of the section on a separate sheet of paper • Label each part clearly!