* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Title - Iowa State University
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
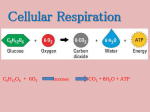
Leader: Course: Instructor: Supplemental Instruction Date: Iowa State University 1. The breakdown of glucose happens in four stages: 1. 2. 3. 4. Cellular Respiration Chelsea Bio 212(1) Coffman/Howell/Addis 2/6/12 2. Glycolysis involves breaking down glucose to make two molecules of ________. This also creates ___ molecules of ATP and ___ molecules of NADH. Glycolysis requires Oxygen, which is termed ________ respiration. Glycolysis occurs in ___ steps or ___ phases. 3. Pyruvate then enters the mitochondrial matrix, where it is broken down to an ________ group, ___ CO2 group and ___ NADH molecule. 4. Next, the acetyl groups enter into the _____ cycle. They each created two molecules of CO2, one ATP, three NADH and one FADH2. Since there are two acetyl groups, the total yield is ___ molecules of CO2, ___ ATP, ___ NADH, and ___ FADH2. It’s named a cycle because the last step requires the Oxoactate to be synthesized back to ______. This cycle can be controlled through competitive ______. 5. Lastly, the NADH and FADH2 made in the previous step contain high-energy electrons, which is harnessed to produce a ___ electrochemical gradient, which is then used to synthesize _____. This process is called ____________ phosphorylation. ATP ________ is the protein involved in ATP production. The process by which H+ is pumped back across the membrane to create ATP is called _____________. The amount of ATP produced is based on how many molecules of ______ are oxidized. ATP synthase works as a ________ machine, where H+ changes the subunits to turn it clockwise. This machine has three steps: Conformation 1: _____ and Pi bind to the protein. Conformation 2: _____ is produced. Conformation 3: ATP is released. 1. Which of the following occurs in the cytosol? A. Glycolysis B. Breakdown of pyruvate to an acetyl group. C. Citric acid cycle D. Oxidative phosphorylation 2. The source of energy that directly drives the synthesis of ATP is? A. The oxidation of NADH B. The oxidation of glucose C. The reduction of O2 D. The H+ gradient. Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu