* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Biology Review Unit 5 and 6
Survey
Document related concepts
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
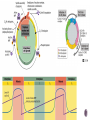
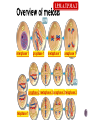
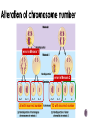
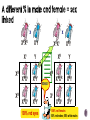
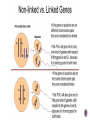
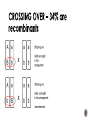
Watch the following Bozeman Biology Episodes (Others under Unit 3) 028 - Cell Cycle, Mitosis & Meiosis 029 - Mendelian Genetics 030 - Advanced Genetics 032 - Signal Transmission 033 - Genotypes & Phenotype 036 - Evolution of Cell Communication 037 - Cell Communication 038 - Signal Transduction in Pathways Overview of cell signaling EXTRACELLULAR FLUID 1 Reception Plasma membrane CYTOPLASM 2 Transduction 3 Response Receptor Activation of cellular response Relay molecules in a signal transduction pathway Signal molecule Figure 11.5 Example of Pathway Steroid hormones bind to intracellular receptors Hormone EXTRACELLULAR (testosterone) FLUID Plasma membrane Receptor protein Hormonereceptor complex 1 The steroid hormone testosterone passes through the plasma membrane. 2 Testosterone binds to a receptor protein in the cytoplasm, activating it. 3 The hormone- DNA mRNA NUCLEUS Figure 11.6 CYTOPLASM receptor complex enters the nucleus and binds to specific genes. 4 New protein The bound protein stimulates the transcription of the gene into mRNA. 5 The mRNA is translated into a specific protein. Other pathways regulate genes by activating transcription factors that turn genes on or off Growth factor Receptor Phosphorylation cascade Reception Transduction CYTOPLASM Inactive transcription Active transcription factor factor P Response Figure 11.14 DNA Gene NUCLEUS mRNA 4 Minute action potential START HERE - RESTING POTENTIAL (Includes multiple other steps) Na+ is high outside the cell K+ is high inside the cell The cell is polarized (negative on the inside and positive on the outside) A signal is received Na+ channels open Na+ diffuses into the cell K+ channels open K+ diffuses outside the cell Depolarization (May include multiple steps) ACTION POTENTIAL (Includes multiple other steps) Na/K pump - pumps Na+ OUT and K+ into the cell Repolarization (Reset) (May include multiple steps) Action potential moves to the axon terminus Ca++ channels open Ca++ moves into the cell Vesicles with neurotransmitters move to synaptic membrane Neurotransmitters diffuse from presynaptic axon through synapse Neurotransmitters bind at postsynaptic membrane (dendrite) of another nerve cell END HERE The signal is restarted Meiosis Crossing over 4 daughter cells all genetically different Sodaria lab Genetics - Monohybrid cross, dihybrid cross, allele, homozygous heterozygous, sex-linked, linked genes, F1, F2, incomplete dominance, codominance I.P.M.A.T.P.M.A.T 2n=4 interphase 1 prophase 1 metaphase 1 anaphase 1 n=2 prophase 2 metaphase 2 anaphase 2 telophase 2 telophase 1 error in Meiosis 1 error in Meiosis 2 all with incorrect number 1/2 with incorrect number Start assuming genes are on different chromosomes – independent assortment Other options Sex-linked Linked genes Codominace Multiple alleles Others? x XR XR Xr XR XR XR Xr XR Xr x X rY Y XRY XRY 100% red eyes XR BINGO! Xr XR X r XRY XR Y XR XR XRY XR Xr X rY 100% red females 50% red males; 50% white males Linked genes are found close to each other on the SAME chromosome Linked genes do not assort independently of each other 2 different cell lines in cat Cross a recessive fly (mutant for both traits) with a fruit fly that is heterozygous for both A = wild type wings (normal) a = mutant wings (vestigial) B = wild type color (yellow) b = mutant color (black) Expected Observed 50 33 Mutant (vestigial wings/black) 50 33 Vestigial Wings, Yellow 0 17 Normal, Black Body 0 17 Wild Type (normal wings/yellow Dihybrid Cross with two plants RrYy x RrYy R = round r = wrinkled Y = yellow y = green Write a null hypothesis: The following are the observed results: complete the chi-square test to determine if the results support your null hypothesis: Round Yellow Peas Round Green Peas Wrinkled Yellow Peas Wrinkled Green Peas 219 81 69 31 Find the full explanation at this link Phenotype Observed (O) Expected (E) O–E (O – E)2 Round Yellow Peas 219 225 -6 36 Round Green Peas 81 75 6 36 Wrinkled Yellow Peas 69 75 -6 36 Wrinkled Green Peas 31 25 6 36 Total 400 400 Phenotype (O – E)2 E (O – E)2 / E Round Yellow Peas 36 225 0.16 Round Green Peas 36 75 0.48 Wrinkled Yellow Peas 36 75 0.48 Wrinkled Green Peas 36 25 1.44 Total 2.56 Chi square = 2.56 Degrees of freedom = # of groups -1 = 4-1 = 3 P = .05 Critical value = 7.81 The chi-square values is less than the critical value so we ACCEPT the null hypothesis. There is no statistical difference between what we expected in the dihybrid cross and the observed result.