* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mitosis
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
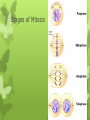
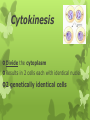
Mitosis Objective: I can identify and describe the stages of mitosis. Warm Up: What makes a cancer cell so dangerous? Cell life cycle: changes cell goes through from time formed until it divides 2 major periods: 1. Interphase: cell grows and carries on usual metabolic activities - longest phase of cycle - very active -DNA is duplicate toward end 2. Cell division: It reproduces itself - fx : more cells for growth and repair processes Interphase G1 Phase: synthesis of RNA and proteins .Period of growth and development for the cell. S phase ( Synthesis): the chromosomes of the cell are copied G2 Phase : cell grows in Preparation for cell division). Any repairs Mitosis Cells replicated Genetic material separates & cell prepares to split into two cells Stages of Mitosis 4 Stages Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Stages of Mitosis Prophase- st 1 stage Stage where dividing cells spend the most time The cells chromatin tightens, or condenses into chromosomes The chromosomes are shaped like an X Each chromosome is a single structure that contains the genetic material Each half of this X is called a sister chromatid. Sister chromatids- structures that contain identical copies of DNA Centromere: structure at the center of the chromosome where the sister chromatids are attached The centromere is important , it ensures that a complete copy of replicated DNA will be part of the daughter cells at the end of the cycle Nuclear envelope breaks down Microtubule structures called spindle fibers form in the cytoplasm *in animal cells another pair of microtubule structures called centrioles migrate to the ends or poles of the cell. Metaphase- 2nd stage Sister chromatids are pulled along the spindle apparatus toward the center and line up in the middle of the cell along the equatorial plate One of the shortest stages Anaphase- 3rd stage Chromatids pulled apart Microtubules of the spindle apparatus begin to shorten Sister chromatids separate into 2 identical chromosomes All the sister chromatids separate simultaneously At the end- the microtubules move the chromosomes toward the poles of the cell. Telophase – Last stage Chromosomes arrive at the poles of the cell and begin to relax, or decondense A new nuclear membrane starts to form around each group. Chromosomes uncoil, and the spindle disappears. Cytokinesis Divide the cytoplasm Results in 2 cells each with identical nuclei 2 genetically identical cells T.O.D. List the stages of Mitosis