* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Non-Mendelian Genetics
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
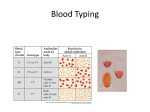
Non-Mendelian Genetics Free PowerPoint Backgrounds For all of the inheritance patterns we will be doing Punnett squares in class. Please leave room in your notes to add those. Free PowerPoint Backgrounds Today, we know that genes often do not follow Mendel’s Laws all the time! There are exceptions….. • • • • • • • • Incomplete dominance Co-dominance Epistasis Polygenics Sex influenced Sex linkage Environmental genes Pleiotropy Free PowerPoint Backgrounds Incomplete dominance • Characterized by a blending of traits. Phenotype of offspring falls somewhere between each parent, when genotype is heterozygotic. These intermediate offspring are called roans. • EX: Red horses (RR) crossed with white horses (rr) produce Rr roans that are “pink” in color. Free PowerPoint Backgrounds Co-dominance • Characterized by the expression of both alleles. Even the recessive allele affects the organism. Free PowerPoint Backgrounds EX: Blood type - A and B are both dominant! • IAIA or IAi= A type • IAIB = AB type B B B • I I or I i = B type • ii = O type Free PowerPoint Backgrounds Epistasis • Characterized where one set of genes (2 alleles) covers or overrides a totally separate set of genes (2 other alleles). Ex: Heterochromia iridum Free PowerPoint Backgrounds Epistasis Ex: Albinism. If an organisms carries the albino gene (a) no matter what genes that organism has for color, the organism will be albino. So a mouse with a B=black coat genotype of BBaa will have NO a= albino color! Free PowerPoint Backgrounds Polygenic traits Characterized by many genes are needed to affect a single trait. Eye color Hair color Free PowerPoint Backgrounds Sex influenced Genes that are expressed differently based on hormones produced by the sex chromosomes X or y. EX: patterned baldness Free PowerPoint Backgrounds Sex linkage Characterized by genes carried on the X or Y chromosomes. • If the genes are on the • Those carried on the X y, they are called are more abundant holandric. Ex: Ear hair • EX: Muscular Dystrophy Free PowerPoint Backgrounds • EX: Hemophilia • XhXh or XhY= hemophilia. • Males CAN’T be carriers of an X-linked gene! Lets do a Punnett Square to show this Free PowerPoint Backgrounds Environmental genes Phenotype that changes as genes are exposed to external stimuli, like temperature. Free PowerPoint Backgrounds Pleiotropy One gene controls multiple expression. EX: Genes for white coat color in dogs also controls the ability to hear. Free PowerPoint Backgrounds