* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2 Types of Chemical Weathering Hydrolysis Oxidation
Flux (metallurgy) wikipedia , lookup
Bottom-blown oxygen converter wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Oxygen therapy wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Surface properties of transition metal oxides wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
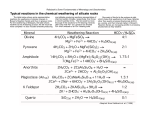
2 Types of Chemical Weathering Chemical Process changes rocks and minerals into new substances Hydrolysis Oxidation is is water dissolving the minerals in rocks the reaction of OXYGEN with METALS to form OXIDES Acids found in water OXIDES weaken the rock and cause the rock to fall apart (Carbonic acid) Help speed up the process of dissolving rocks Example: iron oxide = RUST Caverns KARST Topography result when HYDROLYSIS dissolves Calcite in underground limestone rocks ACID RAIN Oxidation Examples: Caused by Air pollution Helps Speed up Chemical weathering iron + oxygen = rust – iron oxide silver + oxygen = tarnish copper + oxygen = greenish color