* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download COX 2 Inhibitor Interactions - Center for Selective C–H
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
MTOR inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
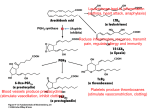
COX 2 Inhibitor Interactions Organic Pedagogical Electronic Network Created by Alyssa Black and Dominic Caputo Edited by Margaret Hilton Honors Organic Chemistry Chem 2321 (Sigman), 2013 COX-2 Inhibitors and the COX-2 Active Site Overview: COX 2 inhibitors were widely used anti-inflammatory drugs until lethal side effects were discovered. These inhibitors interact with the COX 2 enzyme active site, hindering the pathway that leads to several downstream precursor molecules. Key Interactions in the Active Site Wiki Page: COX-2 Inhibitors Other References Selective COX-2 inhibitors by Knaus et al. and COX inhibitory effects by Amini et al. COX-2 Inhibitors and the COX-2 Active Site Overview: COX 2 inhibitors were widely used anti-inflammatory drugs until lethal side effects were discovered. These inhibitors interact with the COX 2 enzyme active site, hindering the pathway that leads to several downstream precursor molecules. Examples of COX 2 Inhibitors Valdecoxib Vioxx Celecoxib Wiki Page: COX-2 Inhibitors Other References Selective COX-2 inhibitors by Knaus et al. and COX inhibitory effects by Amini et al. Acetylation of COX-2 Active Site by Aspirin Aspirin can act as a COX-2 inhibitor, yet it is not as selective as most COX-2 inhibitors. Thus, it will also react with COX-1 enzymes, causing undesired side effects. When aspirin interacts with the COX-2 active site, it permanently acetylates a residue in the active site, according to the following mechanism. Reference: Acetlyation of COX-2 by aspirin by Marnett et al. Problems 1. Based upon the examples of COX-2 inhibitors, what are some possible analogs that could act in a similar way? 2. Which of the following amino acids could interact with a COX-2 active site? (Select all that apply.) a) Lysine b) Glutamic Acid c) Asparagine d) Leucine 3. Propose a mechanism for this step in the synthesis of a COX-2 inhibitor. AcOH, TFA References: Wiki's Amino Acid Page and Synthesis of COX-2 Inhibitors by Reider et al. Contributed by: Created by Alyssa Black and Dominic Caputo (Undergraduates) Edited by Margaret Hilton Honors Organic Chemistry Chem 2321 (Sigman), University of Utah 2013 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons AttributionShareAlike 4.0 International License.