* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grammar Notes - Holly High School
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Semantic holism wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Focus (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sentence spacing wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sloppy identity wikipedia , lookup
Transformational grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Antisymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Bound variable pronoun wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
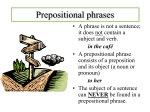
Grammar Notes 24 November 2008 Definitions: Phrase: A group of words that are part of a sentence but do not form a complete thought. It is missing either the subject or the verb. Clause: A group of words that are part of a sentence and contain a subject and a verb but does not form a complete thought. Prepositional Phrase: o A prepositional phrase begins with the preposition, ends with the object of the preposition and includes any adjectives or articles that modify the object of the preposition. o Prepositional phrases can act as adjectives or adverbs. o Prepositional phrases often tell direction. o Look for phrases that begin with words such as: in, between, on, under, around, inside, etc. o Punctuation note! When a prepositional phrase begins a sentence, you must use a comma after the phrase. Example: I found $20 in my pants pocket. prep. object of the preposition adjective Appositive Phrases Appositive phrases Appositive phrases sentence. Appositive phrases Appositive phrases o If they come 25 November 2008 are nouns or pronouns with modifiers. provide additional information and description to the are placed near the noun or pronoun they describe. follow the following comma rules: at the beginning of sentence, comma must follow the phrase. A well meaning procrastinator, Ryan felt guilty for missing his deadline. o If they come in the middle of the sentence, comma must come prior and after phrase. My favorite teacher, a fine chess player in her own right, has won several state-level tournaments. o If they end a sentence, comma must come prior to the phrase. Harry was rough and tough, a boy going through his chin stuck out a mile. Why use them: Create more graceful sentences. Eliminate repetition. Create a beat or rhythm in your writing. Make your writing more interesting. WU: Underline and punctuate the appositives in the following sentences. 1. Sweetbriar a company known throughout the South is considering a nationwide advertising campaign. 2. An above-average student and talented musician John made his family proud. 3. The extremely popular American film Titanic was widely criticized for its mediocre script. 4. The greatest American film ever made Citizen Kane won only one Academy Award. 5. 60 Minutes the TV news magazine program featured a story on the once popular singer Whitney Houston. Absolute Phrases 26 November 2008 A sentence part describing the rest of the sentence in which it appears. Almost complete sentences. As a test, you can make every absolute a sentence by adding was/were. Opening word is often a possessive pronoun: my, his, her, its, our, their Absolute phrases follow the following comma rules: o If they come at the beginning of sentence, comma must follow the phrase. Both cradling guns, two men stood watching the station. o If they come in the middle of the sentence, comma must come prior and after phrase. A teenager in a black tank top, a green tattoo flowing across her back, hoisted a toddler on her hip. o If they end a sentence, comma must come prior to the phrase. Mama was out of bed now, her long black skirt over nightgown. WU: Underline and punctuate the absolute in the following sentences. 1. He looked over to where the huge, filthy birds sat their naked heads sunk in the hunched feathers. 2. Her whole body shaking tears streaming down her face she burst into great sobs. 3. The little boy stared at her silently his nose and eyes running. 4. Greg his elbows spread wide on the arms of his chair stretched his legs further under the table and looked at the fire. 5. Bill ran his legs trembling with fear far from the burning house.