* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download wonderful world of phrases and clauses
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
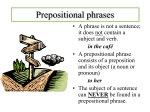
The Wonderful World of Phrases and Clauses “GRAMMAR IS A PIANO I PLAY BY EAR. ALL I KNOW ABOUT GRAMMAR IS ITS POWER.” ~JOAN DIDION General Definitions Phrase-is a group of words that contains a subject OR a predicate (NOT BOTH) Clause-is a group of words that contains a subject and predicate Independent clauses express complete thoughts (can be sentences) Dependent clauses cannot be sentences on their own Identify the (P)phrases, (DC) dependent clauses, and (IC) independent clauses Rita packed a sandwich for lunch. Although she is not a vegetarian, Rita prefers peanut butter sandwiches. Rita reached in her bag for the sandwich when she realized she accidentally brought her dad’s tuna fish sandwich. Prepositional Phrases Prepositional phrases begin with a preposition and end with a noun (in pinks below) The bee buzzed with his bee friends from the beehive, around the garden, then to the tree and over it. The monkey swung from branch to branch through the forest under the sunny sky. Appositive Phrase Is noun or pronoun that restates the noun in the sentence (in blue below) Johnny Depp, a handsome actor, starred in Pirates of the Caribbean. Kiera Knightly costarred in the movie, a huge box office success. Verbal phrases-are verbs used as a different part of speech Gerunds-Nouns Infinitives- Nouns Participles-Adjectives Kevin Spacey as “Verbal” Kint in The Usual Suspects Gerunds Take the progressive form of the verb End in –ing Are used as nouns (subjects, objects of prepositions, direct objects) Crawling to the lake, the snake cooled himself from the hot sun. Sam won the game by hitting the game-ending home run. Talking while chewing gum can lead to accidents. Infinitives Take the infinitive verb forms Start with the word “to” Are used as nouns (subjects, objects of prepositions, direct objects) To be or not to be: that is the question. I want to learn to speak Japanese. CAUTION! Sometimes certain prepositional phrase look like infinitives. If a “to” is followed by a noun, it is being used as a preposition. If it is followed by a verb, then it is an infinitive. I went to the store to buy chocolate milk. Participles and Participial Phrases Take on the progressive form of the verb OR past tense form of the verb End in –ing OR –ed (or sometimes -en/-n/-t) Are used as adjectives (sometimes adverbs) Present Participles End in –ing; used as adj. or adv. The grinning Chesire Cat slowly disappeared from Alice’s view. The losing team ran off the field, crying and moping on the way toward the locker rooms. Don’t get these mixed up with gerunds that end in –ing but are used as nouns! Past Participles End in –Ed, –En , -D, -N, or T Used as Adjectives or Adverbs Covered in slime, the Chemist adjusted his adjusts his formula so to not create a second explosion. The binder, worn from years of misuse, finally lost its cover. Now, you try it… Label (PP) Prepositional Phrase, (A) Appositive, (G) Gerund, (PA)-Participle, or (I) Infinitive Sliding down the banister, Joel Goodson, Tom Cruise’s character in Risky Business, sings along to “Old Time Rock and Roll”. “Writing is a socially accepted form of schizophrenia.” ~Doctrow To write a clear composition, the goal of any AP student, takes time, practice, and a love of words. “With public sentiment, nothing can fail.”~ Abraham Lincoln Prepositional Phrase, Appositive, Gerund, Infinitive, or Participle Sliding down the banister, Joel Goodson, Tom Cruise’s character in Risky Business, sings along to “Old Time Rock and Roll”. “Writing is a socially accepted form of schizophrenia.” ~Doctrow To write a clear composition, the goal of any AP student, takes time, practice, and a love of words. “With public sentiment, nothing can fail.”~ Abraham Lincoln Assignment… Review your “Losing its Grip” paragraph. To help you combine sentences and transition, use and label at least one of each type of phrase: Prepositional Appositive Gerund Infinitive Participial