* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is some basic information about DNA?
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
DNA barcoding wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
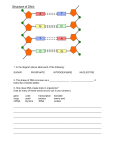
What is some basic information about DNA? Copyright 2016 by the Rector and Visitors of the University of Virginia What is some basic information about DNA? 4 nucleotides make Up DNA: Nucleotides can be thought of as building blocks. These building blocks can be arranged in sequences. The human genome contains about 3 billion of these building blocks. Some sequences of the building blocks encode genes. Some sequences are related to the regulation of gene expression. Scientists know what only a small fraction of these building blocks do (most of the sequences have no known function!). A = adenine T = thymine G = guanine C = cytosine A gene is a sequence of DNA nucleotides: GCAT TCGCCA The building blocks of each gene are unique. This example shows the hypothetical first 10 nucleotides/building blocks of a gene. Double stranded DNA: A T G C pair pair When DNA is not being transcribed, the nucleotides are paired up. A always pairs with T; G always pairs with C. When they are paired, they are referred to as double stranded (2 strands of DNA together). T A CG A T G C = Double stranded DNA If you look at “How are protein products made from a gene?”, you can see how transcription and double stranded DNA are displayed in the nucleus of the cell. Copyright 2016 by the Rector and Visitors of the University of Virginia