* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Parts and Functions
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
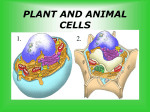
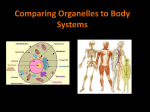
Cell Parts and Functions 1. organelles – structures in eukaryotic cells that carry out the functions of the cell; most are surrounded by a membrane 2. Cell membrane – covers all cells, keeping cytoplasm inside, regulates what enters and exits the cell 3. Cell wall – a rigid structure that encloses, supports, and protects the cells of plants, algae, fungi, and bacteria 4. cytoplasm – the gel-like fluid that is found inside a cell surrounding the organelles 5. nucleus – cell library or brain which controls all the activities of the cell and contains the hereditary material (DNA) 6. DNA – contains the information needed for a cell to make new cells, the hereditary material, found in the nucleus (deoxyribonucleic acid) 7. ribosomes – make proteins; smallest but most numerous organelle 8. endoplasmic reticulum – ER, moves materials around in a cell in a series of folded membranes, can be rough or smooth 9. mitochondria – releases energy or fuel for the entire cell by breaking down food. The energy is called ATP. 10. chloroplasts – in plant cells and algae, green in color, contain chlorophyll that uses light energy to produce sugar (glucose, food) from carbon dioxide and water 11. Golgi bodies – package cellular materials and transport them within or out of the cell 12. vacuoles – stores food, water, waste products, and other liquids, and are very large in plant cells 13. lysosomes – contain digestive chemicals that help break down food molecules, cell wastes, and worn-out cell parts, and even the whole cell when it dies 14. cell – the smallest unit of an organism that can carry on life functions 15. tissue – a group of cells that work together to do one job and each cell has a part to do to keep the tissue alive 16. organ – a structure made of two or more different tissue types that work together to do a job 17. organ system – when a group of organs work together to perform a certain function 18. multi-cellular organism – several organ systems work together to keep an organism alive; all the parts cannot survive on their own; the cells must be in the organism to stay alive Cell Tissue Organs Organ systems Organism 19. unicellular organism – a one-celled organism, it performs all its life functions by itself; does not need other cells to survive 20. Homeostasis – an organism’s ability to keep the proper conditions inside their bodies no matter what is going on outside the organism 21. Living things are organized in structure respond to their surroundings use energy grow and develop reproduce Needs a place to live; environment with what that organism needs, space raw materials – water, proteins, fats, and sugars 22. All cells have cell membranes cytoplasm DNA Ribosomes Two Types of Cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells Bacteria Do not have a nucleus World’s smallest cells Have only ribosomes, cell walls, cytoplasm, cell membranes and DNA DNA is one long, circular molecule shaped like a rubber band First cells on Earth, 3.5 billion years ago 2. Eukaryotic Cells All cells except bacteria Have a nucleus Have many different organelles in the cytoplasm About 10 times larger than prokaryotic cells more complex than prokaryotic cells DNA in the nucleus and linear Plant and fungi have a cell wall, other eukaryotic cells do not First appeared on Earth 2 billion years ago