* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What causes Earth`s surface to change?
Survey
Document related concepts
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
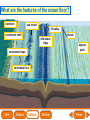
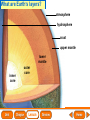
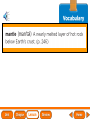
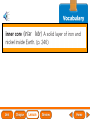
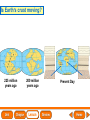
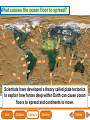
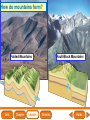
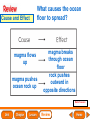
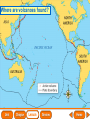
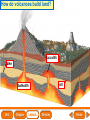
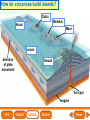
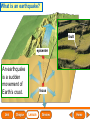
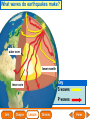
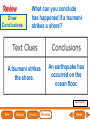
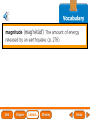
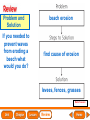
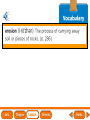
Lesson 1 Earth’s Landforms Lesson 2 Plate Tectonics Lesson 3 Volcanoes Lesson 4 Earthquakes Lesson 5 Shaping Earth’s Surface What causes Earth’s surface to change? landform relief map topographical map atmosphere hydrosphere crust mantle outer core inner core What are landforms? mountain waterfall plateau canyon desert hill valley tributary lake river plain inlet cliff coast ocean delta estuary dune beach What are the features of the ocean floor? continent sea mount rift valley trench continental shelf mid-ocean ridge continental slope continental rise abyssal plain How are Earth’s features mapped? Relief Map of Nunviak Island, AK Topographical Map of Nunviak Island, AK What are Earth’s layers? atmosphere hydrosphere crust upper mantle lower mantle inner core outer core Main Idea What are Earth’s layers? • atmosphere • hydrosphere • crust • upper mantle • lower mantle • outer core • inner core Vocabulary The layer of Earth’s interior below the crust is called the ____________. All of Earth’s liquid and solid water makes up its ____________. The ____________ is made of solid metals. A ____________ is a physical feature on Earth’s surface. The rocky layer of Earth’s surface is called the ____________. crust hydrosphere inner core landform mantle Vocabulary The ________________ includes all of the gases around Earth. A map that uses shading to show elevations is called a ________________. The ________________ is made of liquid metals. topographical map uses lines to show elevation. A ________________ topographical atmosphere outer core relief map map Classify Which features of the ocean floor angle downward and which angle upward? Upward Downward continental slope seamount continental rise mid-ocean ridge continental shelf trenches submarine canyon End of Lesson geologist plate tectonics magma fault Is Earth’s crust moving? 225 million years ago 200 million years ago Present Day What causes the ocean floor to spread? Scientists have developed a theory called plate tectonics to explain how forces deep within Earth can cause ocean floors to spread and continents to move. How do mountains form? Folded Mountains Fault-Block Mountains Main Idea Is Earth’s crust stationary or moving? moving Vocabulary The theory of _____________ explains how forces deep within Earth can cause ocean floors to spread and continents to move. Deep cracks in Earth’s crust are called _________. A _____________ is a scientist who examines rocks to find out Earth’s history and structure. Magma _____________ is hot, melted rock. faults geologist magma plate tectonics Cause and Effect What causes the ocean floor to spread? magma flows up magma pushes ocean rock up magma breaks through ocean floor rock pushes outward in opposite directions End of Lesson volcano lava shield volcano cinder-cone landslide volcano composite volcano island chain hot spot island arc Where are volcanoes found? How do volcanoes build land? laccolith dike batholith sill How do volcanoes build islands? Oahu Molokai Kauai Maui ocean direction of plate movement Hawaii hot spot magma Main Idea What is a volcano? A place where magma reaches and flows onto Earth’s surface. Vocabulary Shield volcanoes ____________________ are built by thinner, fluid lava that spreads out over a large area. A stationary pool of magma is called a ____________________. Once magma reaches Earth’s surface, it is called ____________________. Cinder-cone volcanoes are built by thick lava that is ____________________ thrown high into the air and falls as chunks or cinders. cinder-cone volcanoes hot spot lava shield volcanoes Vocabulary Composite volcanoes are built by layers of ash and ___________________ cinders sandwiched between layers of hardened lava. In areas where an ocean-floor plate is pushed under another ocean-floor plate, an ___________________ is formed. A __________________ is an opening in Earth’s crust. An ___________________ is a line of volcanic mountains. composite volcanoes island arc island chain volcano Infer area closest to the hot spot Where will the next Hawaiian Island be located? The islands are in a line from oldest to youngest. The next island will be located past the youngest. End of Lesson earthquake focus epicenter magnitude tsunami What is an earthquake? fault epicenter An earthquake is a sudden movement of Earth’s crust. focus What waves do earthquakes make? outer core lower mantle inner core Key S waves P waves How is an earthquake’s energy measured? How can people prepare? Buildings in San Francisco have been designed to resist damage from earthquakes. Main Idea What is an earthquake? An earthquake is a sudden movement of Earth’s crust. Vocabulary When the waves reach Earth’s surface, they spread out from a point called the ____________. An ____________ is a sudden movement of Earth’s crust. The place where the slipping begins is called the earthquake’s ____________. When an earthquake occurs underneath the ocean, it can produce a huge wave called a ____________. Magnitude is a measure of the amount of energy ____________ released by an earthquake. earthquake epicenter focus magnitude tsunami Draw Conclusions What can you conclude has happened if a tsumani strikes a shore? A tsumani strikes the shore. An earthquake has occurred on the ocean floor. End of Lesson weathering erosion glacier deposition landslide meander sediment floodplain What is weathering? Weathering is the process through which rocks or other materials are broken down. What is erosion? Erosion is the process through which weathered rock is moved from one place to another. What is deposition? The process by which eroded materials, such as sediments, are dropped off in another place is called deposition. How are shorelines changed? When water collects on land that is normally dry, it is called a flood. How can shorelines be protected? Fences and grasses help keep sand dunes from being eroded by wind. Some barricades may be built to prevent large waves from causing floods. Main Idea What processes break down and build up land? Weathering and erosion break down land, and deposition builds up land. Vocabulary A ____________ is a large mass of slowly flowing ice. Particles of soil and rock that are carried along in water are called ____________. Weathering is the process through which ____________ rocks or other materials are broken down. A ____________ is a place that is easily flooded when river water rises. floodplain glacier sediment weathering Vocabulary Erosion ____________ is the process through which weathered rock is moved from one place to another. Meanders ____________, or gentle loops, sometimes form in rivers with slow-moving water. The process by which eroded materials are dropped off in another place is called ____________. deposition erosion meanders Problem and Solution If you needed to prevent waves from eroding a beech what would you do? beach erosion find cause of erosion levees, fences, grasses End of Lesson