* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Defined - cloudfront.net
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
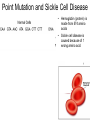
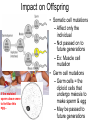
Defined: any change in an organism’s DNA • Where: Single genes or entire chromosomes – Some gene mutations change phenotype (physical characteristics) • Example: Can cause a premature stop codon – Some gene mutations don’t change phenotype. • Example: Could be silent or occur in a non-coding region • When: Throughout the life of the cell Gene: Point Mutations DNA mRNA Amino acids • Defined: one nucleotide is substituted for another • Often repaired by spellchecker enzyme • May lead to amino acid change – See animation • May not lead to any change (Silent Mutation) – Ex: DNA “CCC” is mutated into “CCG” » Same amino acid is created (glycine) Point Mutation and Sickle Cell Disease • Hemoglobin (protein) is made from 574 amino acids • Sickle cell disease is caused because of 1 wrong amino acid Gene: Frame Shift Mutation DNA mRNA Amino acids • Defined: insertion/deletion of a nucleotide • Entire sequence of DNA/RNA after the mutation is shifted (see animation) • Much more serious to the structure/function of the final protein – mRNA sequence may have an early or late “stop codon” Gene: Frame Shift Mutation DNA mRNA Amino acids Impact on Offspring If the mutated sperm above were to fertilize this egg… • Somatic cell mutations – Affect only the individual – Not passed on to future generations – Ex: Muscle cell mutation • Germ cell mutations – Germ cells = the diploid cells that undergo meiosis to make sperm & egg – May be passed to future generations Mutation Causes • Mutagen: agents in the environment that can change DNA – Speed up replication process – Break apart nucleotides • Ex: UV from sunlight breaks hydrogen bond between thymine (T) and adenine (A) Review 1) How are proteins affected if the DNA code is mutated? Example: ATTCGAGG is mutated to ATTCGTGG 2) What is the difference between a point mutation and frame shift mutations? 3) When are mutations passed on to future generations? 4) What are germs cells? 5) What is a mutagen and how do they cause problems? 6) Are all mutations considered bad/dangerous? Explain.