* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproduction of Plants
Survey
Document related concepts
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
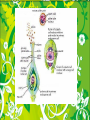
Reproduction of Plants Propagation Sexual and Asexual • Asexual – No seeds – Leaf, stem, or root • Sexual – Union of pollen and egg – Pollination – Fertilization • Pollen tube, male gametes unite with egg cell to form zygote Pollination • Transfer of pollen • Pollen grains – Pores where pollen tubes grow • Self – pollination • Cross – pollination • Wind or animal Gymnosperms • “Naked seeds” • Conifers or Cone – bearers • Pollen cones or seed cones – Seed cones are larger • Pollination occurs in late spring • Seed cones stand up on tips of branches and open slightly • Ovule produces sticky liquid that pollen gets trapped in • Pollination complete seed cone turns upside down Angiosperm • • • • Flowering plants Annual or perennials Ovules develop in ovary Fertilization – Pollen lands on stigma – Pollen tube to enter style – Enters ovary and sperm is released in ovule Parts of the Seed • Hypocotyl – Connection b/w cotyledon and radicle • Radicle – Hypocotyl and embryonic root • Epicotyl – Shoot – stems and leaves • Cotyledons (seed leaves) • Endosperm – Stores plant food • Seed coat – Outer covering protects embryo Seed Dispersal • • • • Ovules develop inside of an ovary Fleshy part nutritious for animals Hooks, spines, or parachutes Large number of seeds Seed Germination • Time between seed is planted, its development until it is self – supporting • Begin once planted or lay dormant – Physical or chemical reactions – Nutrients inside seed During Germination • Embryo swells to burst through the seed coat • Radicle (10 root) – Grows downward – Hypocotyl • connected to cotyledons and radicle • Arches and pushes up through soil – Arch emerges the hypocotyl straightens – Cotyledons and epicotyl are pulled out of the soil • Primary leaves unfold and stem elongates • Primary leaves/true leaves completely emerge – Cotyledons fall off – Photosynthesis begins Improving Chances of Germination • Seeds are primed or enhanced – Stimulate growth hormones in various solutions – Loam, pH, nutrients, and drainage – Scarification – Soaking seeds prior to planting Plant Growth • Regulated by hormones – Stimulate or restrict growth – Auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, inhibitors Plant Hormones • Auxins – Accelerates the growth in stem and leaf • Gibberellins – Stimulate growth in stem and leaf • Cytokinins – Stimulates cell division works with auxins • Inhibitors prevent germination or stem growth – Stimulate fruit ripening by emitting ethylene gas Other factors • Apical dominance – Terminal bud secretes hormones – Inhibit lateral buds on same shoot – Once plant reaches flowering stage bud becomes flower Rooting Hormones • Cuttings • Root – promoting hormones – Indoleacetic acid (IAA), natural – Other forms of this rooting compound used commercially