* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life Cycle of a Plant
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
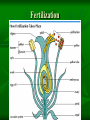
Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant How living things grow, live, and die 4/13/16 Parts of the Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant. 1. 2. 3. 4. Germination Plant Development Fertilization Seed production 1. Germination Seeds are dispersed from parent plant (wind, water, animals): a. they can lay dormant or b. they can grow immediately if conditions are ideal. Early stage of seed growth known as germination. Roots grow downward and stem and leaves grow upward. 2. Plant Development Over time, the seed grows into a mature plant with the structures necessary (male and female reproductive parts) to produce more plants. 3. Fertilization Pollen is produced in the Stamen of a flower. Pollen is transferred from stamen to pistil (pollination) Pollen enters the ovule, located in the ovary leading to fertilization! Fertilization 4. Seed Production One’s the ovule is fertilized, it develops into a seed! Fruit develop to protect the seed. Seeds are structures that contain the young embryo surrounded by the seed coat. Identification Draw and label the following parts of a plant. •Leaves •Roots •Flower •Fruit •Seeds •Stem Life Cycle of a flowering Plant Explain the life cycle of a plant and relate the importance of the proper amount of sunlight to the growth and development of a plant.