* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RECONSTRUCTION
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
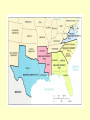
Problems After Civil War • SOUTHERN SOCIETY: whites resent new political power of former slaves, many young men dead, cities in rubble, schools destroyed • SOUTHERN ECONOMY: agriculture crippled, livestock destroyed, banks & businesses closed, railroad tracks destroyed, unemployment • CONGRESS vs. PRESIDENT: each had opposing plans for how to fix problems RECONSTRUCTION • Period of rebuilding & political reorganization of the South after Civil War • 1865 – 1877 • Process for readmitting defeated Confederate states to the Union LINCOLN’S PLAN • Ten Percent Plan • Government would pardon all Confederates who would swear allegiance to the Union • When 10% took oath, Confederate states could form new state governments and send representatives to Congress • Four states qualified: AR, LA, TN, VA • Angered the “Radical Republicans” JOHNSON’S PLAN • From North Carolina • Grants amnesty (pardon) to more than 13,000 former Confederates • Believed that whites must still hold political power in South • Seven remaining Southern states agree, all but Texas set up new governments and send representatives to Congress RADICAL REPUBLICANS • “Radical Republicans” in Congress • Want South to be punished • Try to destroy political power of former slave owners • Propose giving blacks citizenship and the right to vote • Refuse to seat representatives sent by the South to Congress! CONGRESSIONAL PLAN • Set up Freedmen’s Bureau to help African Americans transition to freedom by providing food, teachers, legal aid, horses, mules, etc. • Pass Civil Rights Act of 1866 to give African Americans citizenship and outlaw “black codes” – laws that discriminated against blacks • BOTH are vetoed by Johnson! CONGRESSIONAL REACTION • Congress is mad! • Override Johnson’s vetoes of Freedmen’s Bureau Act and Civil Rights Act • Pass Reconstruction Act of 1867 which did NOT recognize new Southern state governments formed under Lincoln/Johnson plans • Divided former Confederate states into 5 military districts; states had to give former slaves the right to vote in order to reenter the Union • Proposed Civil War Amendments CIVIL WAR AMENDMENTS • 13th (1865): abolished slavery • 14th (1868): gave former slaves citizenship and equal treatment under the law • 15th (1870): said no state can deny right to vote based on race, color, or former servitude JOHNSON IMPEACHED • Radicals believed Johnson was blocking Reconstruction • Impeached him for firing Secretary of War • Technical violation of Tenure of Office Act • House impeached but Senate voted NOT to convict so he stayed in office • Lost 1868 election to Ulysses S. Grant RESULTS OF RECONSTRUCTION • Political struggles in Republican party in the South: scalawags (poor whites), carpetbaggers (northerners who moved South), former slaves • First public schools set up • African Americans elected to office (16 to Congress, more in local governments) • Sharecropping: poor farmers worked land they didn’t own for a small percentage of the crop END OF RECONSTRUCTION • Bank failures lead to 5-year depression • Democrats begin to regain control, Radical Republicans lost power • Amnesty Act gave right to vote back to 150,000 former Confederate officers & returned confiscated estates • Some whites used violence to intimidate African Americans • Ku Klux Klan formed – est. 20,000 killed Why might this time period be called “The Second Civil War”? Did Reconstruction mend the conflict between the North and South, or did it make it worse?