* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.3 Cellular Transport
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
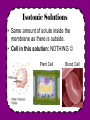
“Materials move across the cell’s membranes” Section 2.3 Do Now • What is the purpose of the cell membrane in a cell? • What goes in and out of our cells? • Why are our membranes important? Objectives • To explain the different functions of the macromolecules in the plasma membrane. • To understand the process of diffusion. • To compare and contrast active and passive transport. Membranes • “Fluid Mosaic Model” Membrane Components • Phospholipids: – Gives the general structure of the membrane Membrane Components • Proteins: allow bigger substances to pass through, also provide structure Membrane Components • Cholesterol: helps maintain structure of phospholipids, prevents them from sticking Membrane Components • Carbohydrates: receptors that send and receive signals. Simulation Activity • Everybody Stand up!!! Lets make a membrane out of the desks. • I need 4 volunteers (1-H2O, 3-Glucose) Types of Transport • Passive Transport • Active Transport • Vesicular Transport Passive Transport • Do NOT require energy • Go from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration • “Go with the flow” 3 Types of Passive Transport • Diffusion • Facilitated Diffusion • Osmosis Diffusion • Molecules move from a high concentration to a low concentration to create DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM. Effected By… • Heat- higher temp increases rate • State of Matter – Solid- slow – Liquid- faster – Gas- fastest • Size and Concentration – Bigger= slower – More concentration = faster Perfume Demo Food Coloring Demo Facilitated Diffusion • the molecules need a “helper” or “facilitator” to allow them to cross the membrane when they are too big. Do NOW • What is passive transport? • What are 2 examples of passive transport? • Explain what happens when you put a sugar cube in your tea in regards to diffusion. Objectives • To understand how the process of Osmosis works. • To explain the different types of solutions • To compare and contrast endocytosis vs. exocytosis. Osmosis - The flow of WATER from a high concentration to a low concentration - Occurs based on the types of solutions you are working with. Solution - A) a mixture in which you cannot separate the components (ex: Kool aid) - i. solute: the substance being dissolved - Ex: kool aid powder - Ii. solvent: The substance doing the dissolving - Ex: water Solutions - Solutions can be… - Isotonic - Hypertonic - hypotonic Isotonic Solutions • Same amount of solute inside the membrane as there is outside. • Cell in this solution: NOTHING Plant Cell Blood Cell 11,397x HYPERtonic Solutions • More solute, less solvent • Cell in this solution:shrinks/shrivels “Plasmolysis” “Crenates” HYPOtonic Solutions • Less solute, more solvent • Effect: cell swells or bursts! / High or low Solute? Cell in ________ Solution H2O H 2O Cell in ________ Solution H 2O H 2O Cell in ________ Solution H 2O H 2O Scenario 1 A salt water fish is put into a freshwater aquarium. • What type of solution is the freshwater? • What is going to happen to the cells of the fish? Scenario 2 A patient is given an IV, which contains the perfect balance of glucose • What type of solution is in the IV? • What is going to happen to the cells of the human? Scenario 3 Your garden is infested with slugs so you go around pouring salt on them • What type of solution is this salt? • What is going to happen to the cells of the slug? (don’t do this to the poor slugs ) Practice • By yourself or with a partner (anyone), work on the diffusion problems. • First try to do this by yourself, then verify your answers with a partner. Try to help each other. If you are confused, raise your hand and I will come help you!! • If you finish early, try to answer the “Think about it” questions on my desk! If you don’t finish, please finish it for homework.