* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download If so, is trkB mRNA in SNB motor neurons
Survey
Document related concepts
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
De novo protein synthesis theory of memory formation wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
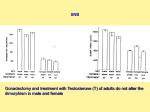
Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and tyrosine receptor kinase b (trkB) by androgens in the motoneurons of the spinal nucleus of the bulbocavernosus (SNB) Erich N. Ottem, Laurel A. Beck, S. Marc Breedlove, and Cynthia L. Jordan Neuroscience Program, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824 completely restore dendritic arborization in castrated adult male rats (Yang et al, 2004). BDNF may act as a classic peptide neurotransmitter, an autocrine factor, or paracrine factor. BDNF may be synthesized in a presynaptic neuron or may originate at a postsynaptic site be retrogradely transported to the presynaptic neuron (Lu,B., 2003). Questions ** (P<0.0056) 100 75 50 25 0 Sham GDX 125 100 75 50 25 0 GDX (14 days) Sham GDX If so, is trkB mRNA in SNB motor neurons regulated by androgens? Methods 2 groups of adult (90-100 days) male Sprague-Dawley rats: Sham operated (n=6), sacrificed 14 days after operation Gonadectomized (GDX; n=6), sacked 14 days after GDX trkB mRNA in SNB motoneurons 175 * 150 (P<0.041) 125 100 75 50 25 0 Sham GDX BNDF mRNA in RDLN motoneurons 150 200 trkB mRNA in RDLN motoneurons (pixels/cm2) Do SNB motor neurons contain trkB mRNA? trkB mRNA in SNB motoneurons (pixels/cm2) If so, is BDNF mRNA in SNB motor neurons regulated by androgens? GDX + Blank 175 Do SNB motor neurons contain BNDF mRNA? 200 GDX + T Sham GDX trkB mRNA in RDLN motoneurons 175 150 125 100 75 Fluorescent ICC using antibodies to detect fluorogold, VGLUT1, and trkB in a Sham GDX rat. Immunorectivity for trkB was observed in SNB motoneurons. Many terminals contacting SNB motoneurons contained VGLUT1 and trkB. Red arrowheads: trkB immunoreactivity in SNB soma. White arrowheads: VGLUT1-positive appositions to SNB dendrites. White arrows: terminal structures positive for both VGLUT1 and trkB. 50 25 0 GDX (14 Days) GDX (14 Days) Sham GDX GDX (14 Days) Experiment 1: In situ hybridization histochemistry using 35S-labeled cRNA probes to detect BDNF mRNA in SNB and RDLN motoneurons SNB and RDLN motoneurons express BDNF mRNA Castration does not change the number of dual labeled VGLUT1 and trkB contacts on SBN or RDLN motoneurons Background: Study 2 BDNF localized to dendrites is implicated in the targeting of a variety of postsynaptic density proteins to dendritic motors (Schratt et al., 2004) . Number of contacts containing both VGLUT1 and trkB immunoreactivity contacting fluorogold-labeled SNB dendrites Experiment 2: In situ hybridization histochemistry using 35S-labeled cRNA probes to detect trkB mRNA in SNB and RDLN motoneurons BDNF enhances glutamatergic signaling via activation of the trkB receptor (Matsumoto et al., 2005). In some systems BDNF is co-released with glutamate to enhance glutamatergic signaling (Lowenstein and Arsenault, 1996). Questions Do glutamatergic neurons innervate SNB motoneuron dendrites? Methods 3 groups of adult (90-100 days) male Sprague-Dawley rats: 1. Sham GDX (n=5), BC and footpad muscles inj. 15mg Fluorogold (FG; Fluorochrome Inc.) , sac’ed d14. 2. GDX + TP (n=5), BC and footpad muscles inj. 15mg FG, sac’ed d14 3. GDX + Blank (n=6), BC and footpad muscles inj. 15mg (FG), sac’ed d14 Experiment 1: Triple-label Confocal ICC A. 1o Abs ; Rabbit antI-FG ( Chemicon), guinea pig antI-VGLUT1 (Chemicon), and sheep anti-BDNF (Chemicon). B. 2o Abs: donkey anti-rabbit-Alexafluor 488 (Molecular Probes), donkey antiguinea pig-Cy5 (Jackson Immuno) , and donkey anti-sheep-Texas Red (Jackson). Experiment 2: Triple-label Confocal ICC trkB mRNA (black silver grains) in SNB (A) and RDLN (B) motoneurons from a sham GDX rat detected with 35S-labeled cRNA probes. SNB and RDLN motoneurons were counterstained with cresyl violet (blue stain). All SNB and RDLN detected were positive for trkB mRNA. Scale bars, 5 mm. A. 1o Abs ; RabbIt antI-FG (Chemicon), guinea pig antI-VGLUT1 (Chemicon), and chicken anti-trkB (Chemicon). B. 2o Abs: donkey anti-rabbit-Alexafluor 488 (Molecular Probes), donkey anti-guinea pigCy5 (Jackson Immuno) , and donkey anti-sheep-Texas Red (Jackson). 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 Sham BDNF was expressed extensively through the SNB motoneuron dendrites of Sham GDX (Column 1) and GDX+T (Column 2) male rats. BDNF expression was much reduced in SNB dendrites of the GDX+Blank (Column 3) treatment group (Column 3). Arrowheads: VGLUT1-positive appositions to SNB dendrites. Arrows: BDNF labeling in SNB dendrites. Castration decreases BDNF in Fluorogold-labeled dendrites of SNB, but not RDLN, motoneurons 60 50 40 30 20 ** (P<0.0078) 10 0 Sham GDX + T GDX + Blank % fluorogoldlabeled RDLN dendritic length containing BDNF immunoreactvity SNB and RDLN motoneurons express trkB mRNA Is the expression of BDNF or trkB protein in either region dependent on androgen? 90 0 % fluorogoldlabeled SNB dendritic length containing BDNF immunoreactvity If so, do glutamatergic terminals or the glutamatergic post- synaptic region contain either BDNF or trkB receptor proteins? BDNF mRNA (black silver grains) in SNB (A) and RDLN (B) motoneurons from a sham GDX rat detected with 35S-labeled cRNA probes. SNB and RDLN motoneurons were counterstained with cresyl violet (blue stain). All SNB and RDLN detected were positive for BDNF mRNA. Scale bars, 5 mm Triple-label ICC for FG, VGLUT1, and trkB Number of contacts containing both VGLUT1 and trkB immunoreactivity contacting fluorogold-labeled RDLN dendrites After bilateral axotomy, BDNF and testosterone are both required to 125 200 2 regulation (Al-Shamma and Arnold, 1997). 150 BNDF mRNA in SNB motoneurons (pixels/cm ) Following axotomy, animals treated with BDNF show less AR down- BDNF mRNA in RDLN motoneurons Blocking neurotrophic receptors (including trkB) halts masculinization of SNB motoneurons in testosterone treated females (Xu et al, 2001) Triple-label ICC for FG, VGLUT1, and BDNF Castration decreases BDNF and trkB mRNA in androgen-dependent SNB, but not RDLN, motoneurons BDNF mRNA contained in SNB motoneurons (pixels / cm2) Background: Study 1 60 50 GDX + Blank 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Sham GDX + T GDX + Blank Summary and Future Directions Castration decreases BDNF mRNA in SNB motoneurons and BDNF protein in SNB dendrites. Because BDNF is implicated in the targeting of post-synaptic density proteins (PSDs) in dendrites, castration may also cause a decrease of several PSDs in SNB dendrites. References Xu, J, GingrasK. M. , Bengston, L., Di Marco, A., and Forger, N.G. (2001) J. Neurosci. 21:4366-4372. Al-Shamma, H.A. and Arnold, A.P. (1997) PNAS.94:1521-1526. Yang, L.Y., Verhovshek, T., and Sengelaub, D.R. (2004) Endocrinology. 145:161-168. Lu, B. (2003) Learn. Mem. 10:86-98 Schratt, G.M. et al., (2004) J Neurosci. 24: 7366-7377. Matsumoto, T et al., (2005) Mol Cell Neurosci. [Epub ahead of print]. Lowenstein, D.H. and Arsenault, L. (1996) J. Neurosci. 16: 1759-1759. 40 30 20 10 0 GDX + T 90 Acknowledgements Sham GDX + T GDX + Blank The project was funded by NIH grant# NS045195 to CLJ and NIH grant # NS28421 to SMB