* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Mitogen-activated protein kinase wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
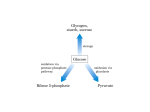
• C H A P T E R 15 • • PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY • • • • • • • • • • • • PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY Function: To supply reducing equivalents for biosynthesis (NADPH) and pentoses for DNA and RNA biosynthesis. Location: Everywhere. Connections: To glycolysis and glycogen through glucose 6-phosphate. Shares some enzymes with glycolysis. To DNA-RNA synthesis through ribose 5-phosphate. Regulation: NADPH inhibits. NADP activates. High glucose 6-phosphate activates. EQUATIONS: Making NADPH: 3 Glucose 6-P 6NADP ¡ 2 fructose 6-P glyceraldehyde 3-P 3CO2 6NADPH 6H Making ribose 5-P: Glucose 6-P 2NADP ¡ ribose 5-P CO2 2NADPH 2H 183 BG McGraw-Hill: Gilbert, Basic Concepts in Biochemistry, JN 5036 • • 184 • Basic Concepts in Biochemistry The hexose monophosphate pathway has several names just to confuse you. It’s called the hexose monophosphate shunt or pathway (HMP shunt or pathway), or the pentose phosphate pathway, or the phosphogluconate pathway (Fig. 15-1). The pathway in its full form is complicated and has complicated stoichiometry. Usually it’s not necessary to remember all of it. The important points are that it makes NADPH for biosynthesis and riboses (C-5 sugars) for DNA and RNA synthesis. NADPH is a reducing agent that is reserved for biosynthetic pathways—notably fatty acid synthesis. Thus, the HMP pathway is called upon when reducing equivalents and fatty acid synthesis are turned on. Primarily, the regulation of the pathway is through the supply and demand of NADPH. NADPH is also used to keep the cellular (and mitochondrial) glutathione in the reduced form through the action of glutathione reductase:1 GSSG NADPH H ¡ 2GSH NADP glycogen NADPH gluconolactone 6-phosphogluconate CO2 glucose-6-P * NADPH ribulose-5 phosphate (C5) glucose glucose-6-P dehydrogenase glycolosis gluconeogenesis ribose-5-P 4, 5, 6, & 7 carbon sugars transketolase (thiamin) transaldolase Figure 15-1 The Pentose Phosphate Pathway 1 Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide, -glutamylcysteinylglycine. The -glutamyl part means that the amino group of the cysteine is attached to the side chain carboxyl group of the glutamic acid rather than to the -carboxyl. GSH is a thiol (sulfhydryl)-containing molecule that can be oxidized to the disulfide, GSSG, by cellular oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide. It helps protect cells against damage that can be caused by oxidants. BG McGraw-Hill: Gilbert, Basic Concepts in Biochemistry, JN 5036 15 Pentose Phosphate Pathway • 185 • This reaction also protects proteins with cysteine residues from becoming oxidized to the disulfide since the GSH can be used to reduce the protein disulfide back to the thiol form: Protein—SS—Protein 2GSH ∆ 2 protein—SH GSSG A somewhat more trivial thing to remember about the HMP pathway is that this is one of the places you’ve seen the vitamin thiamin pyrophosphate. This cofactor is necessary for the transketolase reaction that is in the middle of the HMP pathway. The transketolase reaction converts two C-5 sugars to a C-7 and a C-3. The other place you’ve seen thiamin pyrophosphate as a cofactor is in the pyruvate dehydrogenase and -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase reactions. BG McGraw-Hill: Gilbert, Basic Concepts in Biochemistry, JN 5036