* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download wwii-notes-teacher-edition
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
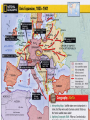
The bigger picture: Global Struggles Last Chapter: Ch. 14-15: The Great Depression & the New Deal •Vocabulary 16/17 •Video Clips: • “Pearl Harbor” “America The Story Of Us” • Review Sheet • TEST A World in Flames & World War II is Dictators Threaten World peace The Holocaust America Moves Toward War 1. 2. 3. The Cold War Begins about how economic problems contributed to political unrest & American involvement in a global conflict. War in Europe Key Self-Test Questions for the Chapter: Ch. 18: This Chapter: Chs. 16-17: Activities: Next Chapter Mobilizing for Defense The Home Front The War for Europe & Africa The War in the Pacific How did the United States become involved in the war and defeat Germany and Japan? Explain how the United States mobilized its economy for war and created opportunities for women & minorities. Explain the tactics the Allies used to defeat Germany, Italy, and Japan. Unit or Background: Ch. 16-17: A World in Flames & World War II Lesson Topic: America & the World is The Rise of Dictators Italy: about how anti-democratic governments came to power in Europe & Asia.. Benito Mussolini, a.k.a. “Il Duce” (the chief) ruled as dictator ~Founded the Fascist Party ~Used his elite guard, the BLACKSHIRTS, to intimidate & suppress all opposition ~Sent Italian troops to ETHIOPIA in 1935 so that Italy could become an imperialist nation Germany: ADOLF HITLER =became Fuhrer(leader) with support from NAZIS (Nat’l Socialist German Workers Party) =blamed Jews, Communists, USSR: (aka: Soviet Union) and intellectuals for the Great Joseph Stalin Used underhanded tactics to take control after Lenin’s Depression =called his gov’t the THIRD death. set up a TOTALITARIAN STATE (a country where the gov’t REICH has complete control) =elite guard, the used the RED ARMY to enforce policies and to crush BROWNSHIRTS, crushed all opposition (==approx. 30 million ppl may have died as a result political opposition of forced labor camps and “purging” of enemies). took control of pvt. lands and made them into state-run farms ==widespread famine Name I. M. Nottaniceguy Hitler’s Rise to Power in Germany Hitler’s views win him many supporters. The Nazi Party wins 40% of the vote in national elections. Hitler is appointed chancellor of Germany Hitler claims dictatorial powers; Hitler crushes political opposition. Lesson Topic: Unit or Background: Ch. 16-17: A World in Flames & World War II America & the World is Militarists Gain Control of Japan 1. about How governments came to power and what were their goals? Japan thought that it had a “divine” mission to lead Italy Asia into a new era of 1. Bad economy led to Italians economic expansion & wanting a stronger leader. prosperity and didn’t want to have to rely on foreign imports. 2. Emperor Hirohito 2. Benito Mussolini takes advantage of this – he was a powerful speaker and convinced his people to trust him. ruled Japan, but the military 3. Fascist- he stressed “ran” the gov’t. Hideki TojoNationalism – interests of state Prime Minister, Japan over the individual. becomes Militaristic & 4. He wants Italy to become a Imperialistic ~invaded Manchuria World Power (1931) ~invaded China (1937) FDR & Internationalism Americans worried about being dragged into another foreign conflict ~~So the U.S. adopted a policy of partial ISOLATIONISM. Americans shunned membership in international organizations like the League of Nations and the World Court. Name Lee V. Ussalone AmericAns’ Concerns After World War I Many Americans are worried about entering another foreign conflict… U.S. Foreign Policy After World War I The United States follows a foreign policy of partial isolationism. The country declines membership in the League of Nations and the World Court… Lesson Topic: Unit or Background: World War II Begins Ch. 16-17: A World in Flames & World War II is the start of WWII in Europe. The Munich Crisis & Appeasement 1. U.S. and Soviet relations were mended and took a stand against fascism. 2. Germany & Italy formed a military alliance known as the AXIS POWERS …Japan later joined. 3. European leaders adopted a policy of appeasement after Hitler took the Sudetenland -(claiming to reunite the German- The War Begins France & Gr.Brit. (ALLIED POWERS) announced that they would go to war against Germany if Poland was attacked… Nonaggression Pact was signed b/t Soviet Union & Germany ~~stated that they would not attack each other…& would later divide up Poland! Germany invaded Poland which started WWII. On September 1,1939, ~Hitler sent in the “Luftwaffe” speaking people of Europe & this would be his last demand to take over land.) 4. U.S. remained neutral, despite Germany’s aggression. about (German Air Force) Blitzkrieg=the lightning war waged by Germany against Western Europe Unit or Background: Ch. 16-17: A World in Flames & World War II Lesson Topic: The Holocaust is Nazi Treatment of the Jews •Hitler’s master plan was the genocide of several different types & races of people. High on the elimination list were Gypsies, Jews, homosexuals, mentally disabled, & religious & political prisoners. •These people were separated from the general population and sent to concentration camps. These camps were awful. No running water, little food, and the prisoners were killed randomly by torture, experiments, gas, or cremation. ~11 million died total (6 million Jews & 5million Gypsies, Russians, Poles, etc.) about the horror Hitler created against those he saw as inferior. Holocaust Losses by Countries Country Pre-War 1939 After -War 1945 Survival Rate Remarks Poland 3,250,000 50,000 1.5% 250,000 that survived in Russia are excluded Russia 2,100,000 600,000 28% - Rumania 800,000 430,000 53% - Hungary 400,000 200,000 50% - Czechoslovak ia 315,000 44,000 14% - France 350,000 275,000 78% Including foreign refugees Germany 240,000 80,000 33% - Netherlands 140,000 20,000 15% - Italy 50,000 33,000 66% - Yugoslavia 75000 12,0 14% - Unit or Background: Ch. 16-17: A World in Flames & World War II Lesson Topic: America Enters the War is FDR Favors Britain •Election of 1940: F.D.R. won a third term vs. Wendell Wilkie by promising to keep us out of war,… if possible! •Congress passed Lend-Lease Act which lent arms & supplies to Allies. •Allied troops in France quickly fell to Nazis and escaped to Britain. •WINSTON CHURCHILL / Battle of Britain- He became England’s new Prime Minister and sent in the R.A.F.(Royal Air Force) to defeat Germany’s attempts to invade Britain.=Germany’s 1st defeat •June 1941=Germany invaded Soviet Union in a surprise attack. about the events that led the US into WW II. Japan Attacks the US •Japan began pushing SW and taking over French military bases in Indochina. US protested by cutting off trade with Japan. •Japan seemed to want peace with the US and peace talks were ongoing. But the US found out Japan was preparing to strike. •December 7, 1941=Japan attacked Pearl Harbor, Hawaii! (a US territory) •“…a date which will live in infamy.” –F.D.R. * FDR asked the US Congress for a declaration of war against Japan on December 8th, 1941.. * The Japanese hope was to cripple the US Navy (especially the aircraft carriers) before the US got into the war. The plan was NOT successful. Germany declared on the US. Hitler believed the Japanese would easily defeat the US & then assist Germany in defeating the USSR (Russia). Lesson Topic: Unit or Background: Ch. 16-17: A World in Flames & World War II The Home Front is Promoting the War Families displayed banners with stars in their home’s windows. The stars represented family members serving in the military. about life in the US during WW II. Rosie the Riveter •Women went to work in the factories replacing the men fighting overseas. Hollywood made films to encourage support for the war. •The government tried to lessen the discrimination in the work place during the war. Life During The War Gas, meat, rubber tires, and nylons were rationed during the war. Americans “made do” w/alternatives (margarine, etc.) •Japanese-Americans were most discriminated Coastal cities practiced nighttime blackouts in case of attack. A Gold Star Banner against. Many are sent from their homes in California, Oregon, or Washington state to internment camps in Wyoming & Utah because we feared they were spies. Unit or Background: Ch. 16-17: A World in Flames & World War II Strengths & Weaknesses Axis Powers: +Strengths: Prepared militarily; firm control of the invaded areas. --Weaknesses: Germany had a two front war going;Japan had no natural resources. Allied Powers: +Strengths: Size of USSR; production potential of the US. --Weaknesses: Not prepared for a long war… Early Fighting in Europe & the Mediterranean US & British troops moved through N. Africa to retake Europe. Soviet troops, with the assistance of a scorched earth policy & a harsh Russian winter, stopped the advancing German troops at Leningrad. Lesson Topic: The War in Europe is about the war against Germany & Italy, 1942-1945. Allied Attacks In the Mediterranean Defeating Germany The Allies stopped the last German counter-offensive in late December, 1944 at the Battle of the •Allied troops attacked the Bulge. Axis Powers in North Africa FDR, Churchill, & and then moved to take Sicily Stalin met at the Yalta and Italy. Conference to discuss post war peace. Operation Overlord After the Battle of the Bulge, the Allies raced with the USSR to see who could get to Berlin first. The invasion of France was code named “Operation Overlord”. The Allies (mostly US & British troops) attacked April 30, 1945 where the terrain was worse, Hitler committed suicide. but there were fewer troops. The attack started June 6, May 7, 1945 Germany surrendered 1944 at Normandy, Anzio, & Omaha beaches. (D-Day) to the Allies (V-E Day); the war in Europe was over!!!! Lesson Topic: Unit or Background: Ch. 16-17: A World in Flames & World War II The Early War in the Pacific •The Japanese military was successful early in the war taking Java, New Guinea, & the Philippines. The War in the Pacific is the war against Japan, 1942-1945. •Captured US soldiers were sent on the Bataan Death March. Japan’s treatment of POWs was brutal. •April 18, 1942 the Doolittle raid bombs Tokyo & increased US spirits. Pacific Offensives The US Navy went “ island hopping”, slowly capturing areas once controlled by the Japanese. The Marines in the Pacific. about & Navy did much of the fighting The Japanese burrowed into tunnels on many islands making it difficult to remove them. The Japanese usually tortured and/or killed POWs. They did not allow for post-battle peace to bury the dead, and they shot medics first because they helped save lives… Victory in the Pacific The Battle of Leyte Gulf was the last, largest, & most decisive naval engagement. It also was the last stepping stone in retaking the Philippines. The bloody Battles of Iwo Jima & Okinawa caused over 50,000 US casualties & 130,000 Japanese casualties, but these US victories gave the military the air bases it needed to begin bombing Japan day & night. Pres.Franklin Roosevelt died April 12, 1945 before the war’s end. Unit or Background: Ch.16-17: A World in Flames & World War II Lesson Topic: The War in the Pacific is about the war against Japan, 1942-1945. The Atomic Bomb •The Manhattan Project was the code name for the building of the atomic & hydrogen bombs. •President Harry Truman had the bombs dropped on Hiroshima (8/6/45) & Nagasaki (8/9/45), Japan killing 200,000 Japanese citizens. •Japan surrendered August 15, 1945 (V-J Day).==World War II officially ended.