* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter One Chemistry
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Degenerate matter wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
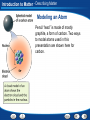
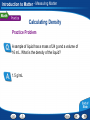
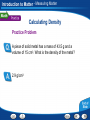
Introduction to Matter - Describing Matter Modeling an Atom Pencil “lead” is made of mostly graphite, a form of carbon. Two ways to model atoms used in this presentation are shown here for carbon. Introduction to Matter - Describing Matter Modeling Molecules Models of molecules often consist of colored spheres that stand for different kinds of atoms. Introduction to Matter - Describing Matter Building Vocabulary A definition states the meaning of a word or phrase by telling its most important feature or function. After you read the section, use what you have learned to write a definition of each Key Term in your own words. Key Terms: matter property chemical molecule mixture chemistry element compound substance heterogeneous mixture chemical formula atom homogeneous mixture physical property chemical solution bond Examples: Matter A In chemical mixture manyiscases, anything isproperty made atoms that of two is combine has a or characteristic mass more toand form substances— takes larger of aup pure particles space. substance called elements, molecules—groups compounds, that describes or its both—that ofability two or tomore are change together atoms into held in Chemistry is the study of the properties of matter and different together the samesubstances. by place chemical but are bonds. not chemically combined. how matter changes. An element is a apure that cannot be or broken A puresubstance substance made In compound chemistry, aissubstance is a single kindofoftwo matter down into any other substances by chemical or In a is heterogeneous mixture, you see more elements chemically combined a setthe ratio. that pure, meaning it always has can a in specific physical parts. means. different makeup—or a specific set of A compound composition—and may be represented by a chemical An atom is the basic particle from which allcompound elements properties. The substances in a homogeneous mixture are so formula, which shows the elements in the are made. evenly that youiscan’t see the different parts. and themixed ratioproperty of atoms. A physical a characteristic of a pure When atoms they a chemical bond, substance that be observed without changing it A solution is combine, ancan example of form a homogeneous mixture. which is a force of attraction between two atoms. into another substance. Introduction to Matter - Measuring Matter Calculating Density A small block of wood floats on water. It has a mass of 200 g and a volume of 250 cm3. What is the density of the wood? Read and Understand What information are you given? Mass of block = 200 g Volume of block = 250 cm3 Introduction to Matter - Measuring Matter Calculating Density A small block of wood floats on water. It has a mass of 200 g and a volume of 250 cm3. What is the density of the wood? Plan and Solve What quantity are you trying to calculate? The density of the block = __ What formula contains the given quantities and the unknown quantity? Density = Mass/Volume Perform the calculation. Density = Mass/Volume = 200 g/250 cm3 = 0.80 g/cm3 Introduction to Matter - Measuring Matter Calculating Density A small block of wood floats on water. It has a mass of 200 g and a volume of 250 cm3. What is the density of the wood? Look Back and Check Does your answer make sense? The density is lower than 1.0g/cm3, which makes sense because the block can float. Introduction to Matter - Measuring Matter Calculating Density Practice Problem A sample of liquid has a mass of 24 g and a volume of 16 mL. What is the density of the liquid? 1.5 g/mL Introduction to Matter - Measuring Matter Calculating Density Practice Problem A piece of solid metal has a mass of 43.5 g and a volume of 15 cm3. What is the density of the metal? 2.9 g/cm3 Introduction to Matter - Measuring Matter Asking Questions Before you read, preview the red headings. In a graphic organizer like the one below, ask a what or how question for each heading. As you read, write answers to your questions. Questions Answers How are weight and mass different? Weight is a measure of the force of gravity on an object. Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. What is volume? The amount of space that matter occupies How is density determined? By dividing the mass of a sample of matter by its volume Introduction to Matter - Measuring Matter Density Introduction to Matter - Changes in Matter Chemical Change A change in matter that produces one or more new substances is a chemical change, or a chemical reaction. Introduction to Matter - Changes in Matter Conserving Matter The idea of atoms explains the law of conservation of matter. For every molecule of methane that burns, two molecules of oxygen are used. The atoms are rearranged in the reaction, but they do not disappear. Introduction to Matter - Changes in Matter Comparing Energy Changes A student observes two different chemical reactions, one in beaker A, and the other in beaker B. The student measures the temperature of each reaction every minute. The student then plots the time and temperature data and creates the following graph. Introduction to Matter - Changes in Matter Relating Cause and Effect A cause makes something happen. An effect is what happens. As you read, identify two effects caused by a chemical change. Write the information in a graphic organizer like the one belowChemical Change Click the Video button to watch a movie Effects about chemical change. A single substance Cause changes to one or more other substances. Chemical change Two or more substances combine to form different substances. Introduction to Matter - Energy and Matter Identifying Main Ideas As you read the section “Forms of Energy,” write the main idea in a graphic organizer like the one below. Then write three supporting details that give examples of the main idea. Main Idea There are many forms of energy. Detail Detail Detail Chemical energy is the energy stored in the chemical bonds between atoms. Electromagnetic energy travels through space as waves. Electrical energy is the energy of electrically charged particles moving from one place to another. Introduction to Matter Graphic Organizer Matter undergoes includes Elements Compounds Heterogeneous Mixtures Physical change Chemical change may be such as such as Crushing Combustion Homogeneous