* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
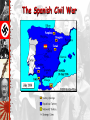
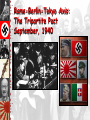
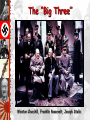
The Versailles Treaty A Weak League of Nations The Ineffectiveness of the League of Nations No progress in disarmament. No effective military force. No control of major conflicts. The “Stab-In-The-Back” Theory German soldiers are dissatisfied. Decadence of the Weimar Republic France – False Sense of Security? The Maginot Line International Agreements Locarno Pact – 1925 France, Germany, Great Britain, Italy Guarantee existing frontiers Establish DMZ 30 miles deep on East bank of Rhine River Refrain from aggression against each other Kellog-Briand Pact – 1928 Makes war illegal as a tool of diplomacy No enforcement provisions The Great Depression The Manchurian Crisis, 1931 Japan invades Manchuria The League of Nations condemned Japan’s invasion of Manchuria in 1931. Japan withdrew from the League. A few years later Japanese armies invade China, starting the Second Sino-Japanese War. Japan Invades Manchuria, 1931 Italy Attacks Ethiopia, 1935 Emperor Haile Selassie Italy invades Ethiopia • Mussolini invaded Ethiopia in 1935. • League of Nations voted sanctions against Italy – League had no power to enforce its punishment of Mussolini. Germany Invades the Rhineland March 7, 1936 The Culprits • Germany: Hitler and • Japan invades the Nazis Manchuria in 1931 and China in 1937 • Italy: Mussolini and the Fascists • Italy invades Ethiopia in 1935 • Japan: Tojo and the Militarists • Germany annexes Austria and the • Spain: Franco and Sudetenland, then the Fascists, Civil takes War 1936 Czechoslovakia and Poland 1937-1939 Causes • Worldwide Economic Depression • Nationalism and Territorial Expansion • Treaty of Versailles causes anger and resentment • Lack of Democratic Tradition leads to rise of dictatorships and militaristic states • German, Italian, and Japanese invasions • Failure of the League of Nations to be an effective organization • Policy of appeasement in Europe U. S. Neutrality Acts: 1934, 1935, 1937, 1939 U.S. Reaction • Citizens want to stay out of the fighting • Strong Anti-war feeling • Neutrality Acts: NO arms sales, NO loans to nations at war, NO arms or loans to nations in Civil Wars Other FDR Policies • Officially recognized Soviet Union 1933 • Non Intervention and no armed forces in Latin America since 1920 “Good Neighbor Policy” • Reduction of Tariffs Invasion of Rhineland • Invasion of Rhineland went against Treaty of Versailles. • Western Democracies denounced Hitler but adopted policy of appeasement. • Appeasement developed for several reasons: – Pacifism – Avoid involvement in a war – Avoid war Germany, Italy, and Japan entered an alliance, known as the Axis powers. Neutrality? • FDR helped China • “…it is peace in our because Japan did not time.” officially declare war • Germany and USSR • FDR preaches against non Aggression Pact. isolationism Later Germany will • Chamberlain and British attack USSR Appeasement: Munich Agreement: Let Hitler take the Sudetenland, Hitler would stop all other aggression. America-First Committee Charles Lindbergh The Austrian Anschluss, 1936 The Spanish Civil War: 1936 - 1939 The National Front The Popular Front [Nationalists] [Republicans] Carlists [ultra-Catholic monarchists]. Catholic Church. Falange [fascist] Party. Monarchists. Anarcho-Syndicalists. Basques. Catalans. Communists. Marxists. Republicans. Socialists. The Spanish Civil War: 1936 - 1939 The Spanish Civil War The Spanish Civil War: 1936 - 1939 The American “Lincoln Brigade” The Spanish Civil War: 1936 - 1939 Francisco Franco The Spanish Civil War: A Dress Rehearsal for WW II? Italian troops in Madrid Liberals vs. Conservatives in Spain • Liberal government passed reforms that upset conservatives. • General Francisco Franco who opposed the new government, started civil war. • Hitler supported Franco, and their fellow fascists. • Soviet Union sent troops to support anti-fascists, or Loyalists. • The governments of Britain, France, and United States remained neutral. • By 1939, Franco had triumphed. “Guernica” by Pablo Picasso The Japanese Invasion of China, 1937 The “Problem” of the Sudetenland German aggression continues • In 1938, Hitler forced the Anschluss, or union with Austria (this was denied under the Treaty of Versailles.) • Hitler sets his sight on Sudentenland. This was a part of Czechoslovakia where 3 million Germans lived. Appeasement: The Munich Agreement, 1938 British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain Now we have “peace in our time!” Herr Hitler is a man we can do business with. Munich Conference • At the Munich Conference, which was held to discuss the situation, British and French leaders chose appeasement and allowed Hitler to annex the territory. Czechoslovakia Becomes Part of the Third Reich: 1939 • In March of 1939, Hitler took over the rest of Czechoslovakia. Rome-Berlin Axis, 1939 The “Pact of Steel” The Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact, 1939 Foreign Ministers von Ribbentrop & Molotov Deal with the Devil • Hitler and Stalin signed the Nazi-Soviet Pact. • They agreed not to fight if the other went to war. • This paved the way for Hitler’s invasion of Poland in September of 1939, which set off World War II. Poland Attacked: Sept. 1, 1939 Blitzkrieg [“Lightening War”] German Troops March into Warsaw European Theater of Operations Blitzkrieg • September 1939, Nazi forces launched a blitzkrieg against Poland. • First the Luftwaffe, German air force, bombed. • Then tanks and troops moved in. • At the same time Stalin invaded from the east, grabbing land. • Within a month, Poland ceased to exist. IT’S WAR • France and Great • France falls, north is Britain declare war occupied by Nazis, on Germany after it South is run by attacks and takes puppet Vichy over Poland Government, Compiegne • Germany takes Denmark, Norway, • Britain will not fall Netherlands, despite bombing Belgium, raids, island, radar, Luxembourg, can break German code • USSR takes Baltic States and Finland The “Phoney War” Ends: Spring, 1940 Dunkirk Evacuated June 4, 1940 Hitler expands • In 1940, Hitler took Norway, Denmark, the Netherlands, and Belgium. • German forces bypassed France’s Maginot Line. • British forces that had been sent to help the French were trapped. • In a desperate scheme, the British rescued their troops from Dunkirk. • French were forced to surrender. • Germany occupied northern France and set up a puppet state, the Vichy government, in the south. Europe • Hitler destroying • Stalingrad: Germans Allied supply ships in occupy, winter, the Atlantic USSR counterattack, • US responds with Soviets win, turning convoys, radar, and point can now move sonar West, 1.1 million • U.S. began to lost, more than the produce more ships U.S. lost in the than were being whole war sunk • War Economy France Surrenders June, 1940 A Divided France Henri Petain The French Resistance The Free French The Maquis General Charles DeGaulle Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis: The Tripartite Pact September, 1940 Now Britain Is All Alone! Battle of Britain • Britain remained defiant, led by Winston Churchill. • In response, Hitler launched bombing raids over British cities that lasted from Sept. 1940- June 1941. • Hitler was unable to take Britain. Over there or not? • “Cash and Carry,” • Increase in Military Warring nations can Spending and Peace buy U.S. weapons as time draft long as they pay cash • Roosevelt wins 3rd and transport them term in 1936, in their own ships promised to keep us • Axis Powers: Italy, out of war Germany, and Japan • “Lend-Lease,” U.S. • U.S sends aid in would lend or lease weapons and ships arms to any nation to GBR. Neutrality whose defense was breaking down vital to us, GBR and USSR U. S. Lend-Lease Act, 1941 Great Britain.........................$31 billion Soviet Union...........................$11 billion France......................................$ 3 billion China.......................................$1.5 billion Other European.................$500 million South America...................$400 million The amount totaled: $48,601,365,000 Lend-Lease Isolationism to Activism • United States declared neutrality at the beginning of the war. • Americans sympathized with those who fought the Axis powers. • Congress passed the Lend-Lease Act 1941, allowing the United States to sell or lend war goods to the Allied powers. • Congress declares war on Japan December 7, 1941, after the bombing of Pearl Harbor. Battle of Britain: The “Blitz” Battle of Britain: The “Blitz” The London “Tube”: Air Raid Shelters during the Blitz The Royal Air Force British Prime Minister Winston Churchill Over There • Increase in Military Spending and Peace time draft • Roosevelt wins 3rd term in 1936, promised to keep us out of war • “Lend-Lease,” U.S. would lend or lease arms to any nation whose defense was vital to us, GBR and USSR The Atlantic Charter Roosevelt and Churchill sign treaty of friendship in August 1941. Solidifies alliance. Fashioned after Wilson’s 14 Points. Calls for League of Nations type organization. Operation Barbarossa: Hitler’s Biggest Mistake Invasion of Russia • June 1941, Hitler nullified the Nazi-Soviet Pact by invading the Soviet Union. • Stalin unprepared, and the Soviet army suffered great losses. • The Germans advanced toward Moscow and Leningrad. • During the siege of Leningrad, more than a million Russians died. • The severe Russian winter slowed the German army. Operation Barbarossa: June 22, 1941 3,000,000 German soldiers. 3,400 tanks. The “Big Three” Winston Churchill, Franklin Roosevelt, Joseph Stalin Axis Powers in 1942 Battle of Stalingrad: Winter of 1942-1943 German Army Russian Army 1,011,500 men 1,000,500 men 10,290 artillery guns 13,541 artillery guns 675 tanks 894 tanks 1,216 planes 1,115 planes Africa • Operation Torch: Allied invasion of Axis controlled N. Africa led by General Dwight D. Eisenhower • Germans surrender in May 1943 • Now on to Italy, Sicily captured in 1943, Mussolini is forced to resign, later is killed • Hold on: Germany will not let Italy go, sends in troops (25,000 allied troops die), Germans had strong resistance The North Africa Campaign: The Battle of El Alamein, 1942 Gen. Ernst Rommel, The “Desert Fox” Gen. Bernard Law Montgomery (“Monty”) Rommel in North Africa • Hitler sent one of his best commanders, General Erwin Rommel, to North Africa. • Rommel had several successes there. • In North Africa, British and American forces, led by Dwight Eisenhower, would trap Rommel’s army, and he would surrender 1943. • After North Africa falls, Allies crossed Mediterranean and landed in Sicily. • Allies victory in Italy led to the overthrow of Mussolini, but fighting continued for another 18 months in Italy. The Italian Campaign [“Operation Torch”] : Europe’s “Soft Underbelly” Allies plan assault on weakest Axis area - North Africa - Nov. 1942-May 1943 George S. Patton leads American troops Germans trapped in Tunisia surrender over 275,000 troops. The Battle for Sicily: June, 1943 General George S. Patton George C. Scott Playing General Patton in the 1968 Movie, “Patton” The Battle of Monte Casino: February, 1944 The Allies Liberate Rome: June 5, 1944 Gen. Eisenhower Gives the Orders for D-Day [“Operation Overlord”] D-Day • Eisenhower and Operation Overlord • 3 million men • Attack at Normandy in N. France • Trickery: Calais • Set for June 5, 1944, bad weather, so it’s JUNE 6, 1944 • Largest land-sea-air operation in army history • U.S. forces at Omaha and Utah Beach • Germans defend with all they have • Saving Private Ryan beginning D-Day (June 6, 1944) D-Day • D-Day was the invasion of France. • Allied troops faced many obstacles but the German troops finally retreated. • As the Allies advanced, Germany reeled from incessant, around the clock bombing. • A German counterattack, the Battle of the Bulge, resulted in terrible losses on both sides. Normandy Landing (June 6, 1944) German Prisoners Higgins Landing Crafts July 20, 1944 Assassination Plot Major Claus von Stauffenberg July 20, 1944 Assassination Plot 1. Adolf Hitler 2. Field Marshall Wilhelm Keitel 3. Gen Alfred von Jodl 4. Gen Walter Warlimont 5. Franz von Sonnleithner 6. Maj Herbert Buchs 7. Stenographer Heinz Buchholz 8. Lt Gen Hermann Fegelein 9. Col Nikolaus von Below 10. Rear Adm Hans-Erich Voss 11. Otto Gunsche, Hitler's adjutant 12. Gen Walter Scherff (injured) 13. Gen Ernst John von Freyend 14. Capt Heinz Assman (injured) The Liberation of Paris: August 25, 1944 De Gaulle in Triumph! U. S. Troops in Paris, 1944 French Female Collaborators The Battle of the Bulge: Hitler’s Last Offensive Dec. 16, 1944 to Jan. 28, 1945 Yalta: February, 1945 FDR wants quick Soviet entry into Pacific war. FDR & Churchill concede Stalin needs buffer, FDR & Stalin want spheres of influence and a weak Germany. Churchill wants strong Germany as buffer against Stalin. FDR argues for a ‘United Nations’. Yalta Conference • “Big Three”– Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin– met to plan end to the war. • Soviets agreed to enter war against Japan and the division of Germany into 4 zones. • However mistrust between the Allies led to the impending “Cold War.” Mussolini & His Mistress, Claretta Petacci Are Hung in Milan, 1945 US & Russian Soldiers Meet at the Elbe River: April 25, 1945 Horrors of the Holocaust Exposed Horrors of the Holocaust Exposed Entrance to Auschwitz Crematoria at Majdanek Holocaust • Systematic murder of 12 million people, half are Jewish, those not deemed a part of Hitler’s master race • Hitler decides on a policy of genocide to kill as many Jews and other “undesirable,” people as he can • We will watch a DVD about U.S. troops finding one of the camps Horrors of the Holocaust Exposed Slave Labor at Buchenwald Not just Jews • As they marched across Europe, the Nazis sent millions to concentration camps to work as slave laborers (remember WWI what did prisoners do?) • Hitler established death camps to kill those he judged racially inferior. • Among many others, some six million Jews were killed in what became known as the Holocaust. Horrors of the Holocaust Exposed Mass Graves at Bergen-Belsen Hitler’s “Secret Weapons”: Too Little, Too Late! V-1 Rocket: “Buzz Bomb” V-2 Rocket Werner von Braun Hitler Commits Suicide April 30, 1945 Cyanide & Pistols The Führer’s Bunker Mr. & Mrs. Hitler V-E Day (May 8, 1945) General Keitel Victory in Europe • Omar Bradley breaks defenses at St. Lo, Patten and his third army advances, Paris freed…. By the French… yes and no • Bulge: Allies capture first German town, German counter offensive pushes into the allied line, but it does not break, Germans can only retreat • US and GBR from the West and South and USSR from the East • USSR reaches Berlin in April of 1945, Hitler kills himself, • May 8, 1945 unconditional surrender of Germany to the Allies, Victory in Europe Reasons for victory for Allies • Reasons for Allies victory: – Because of their location Axis powers had to fight on several fronts. – Hitler made some poor military decisions. – He underestimated the Soviet’s ability to fight. – Huge production capacity of the United States was another factor. – Bombing hindered the German production and caused fuel shortage. V-E Day (May 8, 1945) The Code Breakers of WW II The Japanese “Purple” [naval] Code Machine Bletchley Park The German “Enigma” Machine Pearl Harbor Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto Pearl Harbor from the Cockpit of a Japanese Pilot Infamy • December 7, 1941 • U.S. wants to halt Japanese Imperialism in Asia • U.S cut of trade with Japan that was vital to Japan’s imperial aggression (oil) • U.S. could break Japanese military code and was expecting an attack, but where? • Dec. 6, U.S. breaks code calling for Japan not to accept any peace offerings, issues “war warning” • PEARL HARBOR IT IS • 2 hours, 2,403 dead, 1,178 wounded, 21 ships sunk or damaged, 300 aircraft destroyed, 3 Carriers at sea • U.S. declares war on Japan, Germany declares war on the U.S. Pearl Harbor - Dec. 7, 1941 A date which will live in infamy! President Roosevelt Signs the US Declaration of War USS Arizona, Pearl Harbor Pearl Harbor Memorial 2,887 Americans Dead! “Remember Pearl Harbor” • U.S. citizens are furious • Volunteers (5m) and Draftees (10m) • George Marshall: Army chief of staff begins the Women’s Auxiliary Army Corps (WAAC) to allow women to serve in non combat positions • Minorities in segregated units, did not get to fight in combat until 1945 • Mexicans, American Indians, Blacks, and Chinese and Japanese Americans all sign up to fight. • Tuskegee Airmen: honored for major victories against German air force Pacific Theater of Operations Pacific • US subs and carriers • “I shall return,” not destroyed at after the US loses Pearl the Philippines • Japan was successful • Doolittle’s Raid: at first and took April 18, 1942, 16 US control of most of bombers attack Asia Japanese mainland, symbolic, “Doolittle • General Douglas Do’od It.” MacArthur “Tokyo Rose” Economy • Nations industries • Defense spending (auto) shut down increases and retooled to • More minorities support the war hired to work, FDR effort executive order • Women working in • Scientists: improve men’s jobs radar, sonar, • Aircraft and Ship medicines, production increase Manhattan Project: Atom Bomb War Economy • Fewer consumer products available • Office of Price Administration: Fix prices, increased the income tax, kept prices from going up too high, why? • Selling of war bonds • War Production Board: which companies would convert to make which war materials, drives to collect scrap iron, tin cans, rags, paper, and cooking fat • Rationing: households, ration books to buy food, gas, and other necessities Government interference • Governments took greater role in the economy. – Ordered making of tanks rather than cars. – Consumer goods were rationed, and wages and prices were regulated. – Increased production led to the end of the Great Depression. – Governments limited citizen’s rights, censored the press, and resorted to propaganda. – Women replaced men as “Rosie the Riveter.” Paying for the War Paying for the War Paying for the War Betty Grable: Allied Pinup Girl She Reminded Men What They Were Fighting For • May 1942, the Japanese had gained control of the Philippines, killing thousands during the Bataan Death March. Singapore Surrenders [February, 1942] U.S. Surrenders at Corregidor, the Philippines [March, 1942] Bataan Death March: April, 1942 76,000 prisoners [12,000 Americans] Marched 60 miles in the blazing heat to POW camps in the Philippines. Bataan: British Soldiers A Liberated British POW The Burma Campaign General Stilwell Leaving Burma, 1942 The “Burma Road” War in Pacific • General Douglas MacArthur began “islandhopping” campaign to recapture islands from Japanese. • The captured islands served as stepping stones to the next objective-Japan. • The Americans moved north and were able to blockade Japan. • Bombers pounded Japanese cities and industries. • British pushed Japanese forces back into the jungles of Burma and Malaya. Allied Counter-Offensive: “Island-Hopping” “Island-Hopping”: US Troops on Kwajalien Island Farthest Extent of Japanese Conquests Lt. Col. Jimmy Doolittle: First U. S. Raids on Tokyo, 1942 Battle of the Coral Sea: May 7-8, 1942 Turning Point in Pacific • Coral Sea: US and Australians stop a Japanese invasion of Australia • Midway: Turning point, strategic island that the Japanese do not take, defeat was so large, “avenged Pearl Harbor!” • Island hopping: Allies move from island to island taking them from the Japanese while moving closer to Japan, page 786 • American Indian Code Talkers Turning Point of the War • The years 1942 and 1943 marked the turning point of the war. • In the Pacific, Allied forces won the battles of the Coral Seas and Midway. • Both battles, attacks were launched from aircraft carriers. Battle of Midway Island: June 4-6, 1942 Battle of Midway Island: June 4-6, 1942 Japanese Kamikaze Planes: The Scourge of the South Pacific Kamikaze Pilots Suicide Bombers Turned • Allies begin first • Iwo Jima: 20,7000 offensives in August Japanese, only 200 of 1942 live, U.S loses 6,000 most in any Pacific • “People of the battle, staging point Philippines, I have to attack Japanese returned!” mainland • Kamikazes • Okinawa: 7,600 • Battle of Leyte Gulf, Americans die, Japanese Navy 110,000 Japanese damaged beyond die, last Island repair before mainland Japan Gen. MacArthur “Returns” to the Philippines! [1944] US Marines on Mt. Surbachi, Iwo Jima [Feb. 19, 1945] Tragedy • FDR dies April 12, 1945, Stroke • VP Harry Truman is now president • Nation is devastated Potsdam Conference: July, 1945 FDR dead, Churchill out of office as Prime Minister during conference. Stalin only original. The United States has the A-bomb. Allies agree Germany is to be divided into occupation zones Poland moved around to suit P.M. Clement President Joseph Atlee Truman Stalin the Soviets. The Manhattan Project: Los Alamos, NM Major General Lesley R. Groves Dr. Robert Oppenheimer I am become death, the shatterer of worlds! Manhattan Project • This led the United States building the atomic bomb. • U.S. president, Harry Truman, decided that dropping the bomb would save American lives. • The Allies first issued warnings to the Japanese to surrender or face “utter and complete destruction.” Tinian Island, 1945 Little Boy Fat Man Enola Gay Crew Col. Paul Tibbets & the A-Bomb Hiroshima – August 6, 1945 © 70,000 killed immediately. © 48,000 buildings. destroyed. © 100,000s died of radiation poisoning & cancer later. The Beginning of the Atomic Age The “BOMB” • An attack on the Japanese mainland had U.S. deaths estimated at 1 million • U.S. decides to use a new weapon, the atomic bomb • REPRISAL: August 6, 1945 Hiroshima “Little Boy,”, August 9, 1945 Nagasaki, “ Fat Man” hundreds of thousands die • Enola Gay, name of plane that dropped the first bomb, pilot is Paul Tibbets • Surrender September 2, 1945 U.S.S. Missouri Nagasaki – August 9, 1945 © 40,000 killed immediately. © 60,000 injured. © 100,000s died of radiation poisoning & cancer later. Japanese A-Bomb Survivors Hiroshima Memorials V-J Day (September 2, 1945) Japanese POWs, Guam V-J Day in Times Square, NYC IT’S OVER • Postwar Japan: • Yalta Conference: United Nations for a occupied by U.S. under MacArthur, Germany divided into four occupation war crimes trials, 7 zones die including Tojo, • Nuremburg Trials: seven year Nazi crimes against occupation, freehumanity, death market economy, camps, 24 new democratic defendants, 12 constitution still death, 200 more used today, major tried later world economic power Back Home • U.S. worlds dominant economic and military power (why?) • Economy soared, unemployment down, wages up, farm income tripled • More women in the workforce, though many go back home • California grows by 1 million, more blacks to the North from the South • GI Bill of Rights: education and training for veterans with federal funding of loans for new homes, farms, and businesses • 406,000 casualties, 292,000 deaths WW II Casualties: Europe Each symbol indicates 100,000 dead in the appropriate theater of operations WW II Casualties: Asia Each symbol indicates 100,000 dead in the appropriate theater of operations Country Men in war Battle deaths Wounded Australia 1,000,000 26,976 180,864 Austria 800,000 280,000 350,117 Belgium 625,000 8,460 55,5131 40,334 943 4,222 339,760 6,671 21,878 Canada 1,086,3437 42,0427 53,145 China3 17,250,521 1,324,516 1,762,006 Czechoslovakia — 6,6834 8,017 Denmark — 4,339 — Finland 500,000 79,047 50,000 France — 201,568 400,000 20,000,000 3,250,0004 7,250,000 Greece — 17,024 47,290 Hungary — 147,435 89,313 India 2,393,891 32,121 64,354 Italy 3,100,000 149,4964 66,716 Japan 9,700,000 1,270,000 140,000 Netherlands 280,000 6,500 2,860 New Zealand 194,000 11,6254 17,000 75,000 2,000 — — 664,000 530,000 650,0005 350,0006 — 410,056 2,473 — — 6,115,0004 14,012,000 5,896,000 357,1164 369,267 16,112,566 291,557 670,846 3,741,000 305,000 425,000 Brazil2 Bulgaria Germany Norway Poland Romania South Africa U.S.S.R. United Kingdom United States Yugoslavia WW II Casualties 1. Civilians only. 2. Army and navy figures. 3. Figures cover period July 7, 1937 to Sept. 2, 1945, and concern only Chinese regular troops. They do not include casualties suffered by guerrillas and local military corps. 4. Deaths from all causes. 5. Against Soviet Russia; 385,847 against Nazi Germany. 6. Against Soviet Russia; 169,822 against Nazi Germany. 7. National Defense Ctr., Canadian Forces Hq., Director of History. Massive Human Dislocations The U.S. & the U.S.S.R. Emerged as the Two Superpowers of the later 20c The Bi-Polarization of Europe: The Beginning of the Cold War The Division of Germany: 1945 - 1990 United States vs. Soviet Union • Cold War refers to the conflict between the United States and Soviet Union from 1946- 1990. • Soviet leader Stalin wanted to spread communism into Eastern Europe. • He also wanted to create a buffer zone of friendly countries as a defense against Germany. • By 1948, pro-Soviet governments were in place throughout Eastern Europe. Marshall Plan • Stalin began to threaten Greece and Turkey, the United States outlined a policy called Truman Doctrine. • This meant the United States would resist the spread of communism. • To strengthen democracies in Europe, the United States offered a massive aid package, called Marshall Plan. Berlin Airlift • Western attempts to rebuild Berlin triggered a crisis over the city of Berlin. • The Soviets controlled East Germany, which surrounded Berlin. • To force the Western Allies out of Berlin, the Soviets blockaded West Berlin, but a yearlong airlift forced them to end the blockade. NATO vs. Warsaw Pact • In 1949, the United States and nine other nations formed a new military alliance called North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO.) • The Soviets responded with the Warsaw Pact, which included the Soviet Union and Eastern European nations. The Creation of the U. N. United Nations • In 1945, delegates from 50 nations formed the United Nations. • Under UN Charter, each member nation has one vote in the General Assembly. • It has 5 permanent members: – United States, Soviet Union, Britain, France, and China. • Each has the right to veto any council decision. The Nuremberg War Trials: Crimes Against Humanity Japanese War Crimes Trials General Hideki Tojo Bio-Chemical Experiments Internment • Japanese Americans placed into camps • 110,000 relocated by the order of FDR • Many had to sell homes, businesses, and belongings hastily fearing deportation • Korematsu v. U.S.: FDR was justified in relocation • 1968: $38 million repaid in losses (1/10th of actual losses) • $20,000 per person under Ronald Reagan 7 Future American Presidents Served in World War II The Race for Space Early Computer Technology Came Out of WW II Colossus, 1941 Mark I, 1944 Admiral Grace Hooper, 1944-1992 COBOL language The Emergence of Third World Nationalist Movements The De-Colonization of European Empires