* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants with Seeds
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
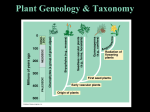
Kingdom Plantae Characteristics • Multicellular Cells have a cell wall • Producers - make their own food • Have a cuticle Waxy layer on stems and leaves keeps plants from drying out • 260,000 species • 2 main groups Vascular Non-vascular • Nonvascular • no specialized tubes to transport water, nutrients and food examples: mosses and liverworts Mosses and Liverworts • Seedless • depend on osmosis and diffusion • plants are small • live in wet environments Mosses and Liverworts • live in wet environments • rhizoids are root like structures to anchor plants • important because they are 1st plants to inhabit a new, bare environment. II. Vascular plants • have specialized tissues to transport water, nutrients and food. Seedless •Ferns, horsetails, and club mosses Seeds •Gymnosperms •Angiosperms Vascular Plants - No seeds • Ferns, horsetails, club mosses • Reproduce with spores Ferns • Underground stem - rhizome • leaf is called a frond • can be very large • like moist environments Horsetails • common millions of years ago • 15 species exist today • less than 1.3 meters tall • look like a bushy horses tail Club Mosses • 25 cm tall • grow in woodlands • common millions of years ago • 1000 species exist today Plants with Seeds • Gymnosperms trees and shrubs that produce seeds in cones naked seeds Pines, spruce, fir & ginkos important for wood for building and paper products Plants with Seeds • Angiosperms • (flowering plants) produce seeds within a fruit fruit trees, roses, oak trees, grasses, cactuses 235,000 species Angiosperms • Flowers attract animals for pollination • Fruits protect and house seeds for survival Monocots • Flower petals in 3’s • leaves with parallel veins Monocots • one cotyledon • bundles of vascular tissue scattered Dicots • Flower petals in 4’s or 5’s • leaves with branching veins Dicots • 2 cotyledons • bundles of vascular tissue in a ring Structures of Seed Plants • Stem Supports plant transport materials • Xylem - transports water and minerals up • Phloem - transports sugar molecules down Roots • Supply plants with water & minerals • anchor plant • store surplus food Leaves • absorbs light energy for photosynthesis • Carbon dioxide + water = Glucose & oxygen The End