* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Draw the schematic, and label the device sizes.
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
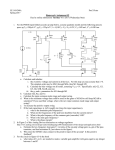
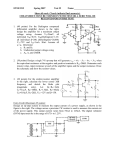
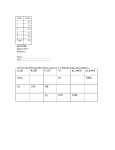
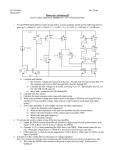
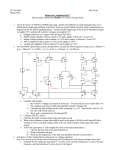
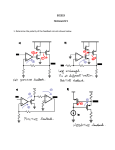
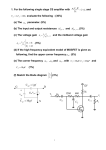
EE 140/240A Spring 2015 Prof. Pister Homework Assignment #5 Due by online submission Wednesday 3/4/2015 (Thursday 9am) 1. Check out the datasheet for the LM324 quad op-amp. http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/lm324.pdf There’s a schematic on page 2. Redraw (or cut and paste) that schematic, and identify (circle and label) a. input differential pair (Darlington) b. current mirror active load c. compensation capacitor d. common drain level shifter e. common emitter amplifier (Darlington) f. output stage 2. Assuming the same process parameters, will the gain for the LM324 design be higher or lower than the amplifier that you built in Lab4? Why? 3. Given a diode-connected NPN transistor Q1 which has a 2uA reference current flowing through it, design a bipolar circuit to generate all four of the current supplies shown in the LM324 schematic. Label your transistors as multiples of each other as appropriate, e.g. Q2=5Q1. 4. Design a 2-stage NMOS input CMOS op-amp with the following specs: a. 80uA tail current b. able to sink 200uA from the load c. output swing to within 200mV of the rails d. input common mode range to within 200mV of the top rail Process specs nCox=200A/V2, pCox=100A/V2, =1/(5V), -Vtp=Vtn=0.5V, VDD=2V, Lmin=0.5um, Cox=5fF/um2, C’ol=0.5fF/um. You may use 1 resistor in your design. Draw the schematic, and label the device sizes. 5. For the amplifier in the previous problem, a. calculate and tabulate Id, Vov, gm, ro, Cgs, and Cgd for all devices b. calculate the 1st and 2nd stage gain, and the overall gain for both differential and common mode signals. c. calculate the common mode input range, and the variation in tail current over that range. d. calculate the gain across Cgd1a. e. calculate the output pole frequency with a 100fF load capacitance. f. calculate the input capacitance of the second stage below the output pole frequency g. calculate the first stage output pole frequency h. calculate the input capacitance of the second stage above the unity gain frequency 6. [ee240A] Are all of the devices in the op-amp above well-modeled by the quadratic model? Are there some input/output ranges where they are, and where they are not? If not, how is that going to affect the performance of the amplifier? 7. [ee240A] If the same amplifier were run at Vov=0, how will that affect the gains and pole frequency?