* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 952 EE Quiz 01 ID#: Name:
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
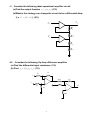
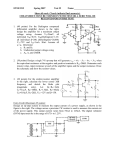
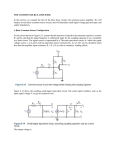
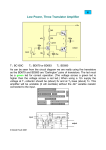
1. For the following single stage CS amplifier with n C oxW 2L 2 mAV 2 and Vtn 1,V A 100 , evaluate the following:(30%) (a) The g m parameter. (5%) (b) The input and output resistances Ri (c) The voltage gain Av vo v i Am vo vs R s 1k RL Rs 0 and Ro RL .(5%) and the midband voltage gain .(5%) R L 2k (d) If the high frequency equivalent model of MOSFET is given as following, find the upper corner frequency H . (5%) (e) The corner frequency C1 , C 2 and CS . with C1 10F , C2 20F and C S 10F (7%) (f) Sketch the Bode diagram C gd 1 pf G 12V D g m v gs v gs C gs 10 pf vo .(3%) vi vs 120k Rs CC1 S 1 68k CS 3k vo CC 2 RL 2. (20 %) For the following single stage MOSFET amplifier with n Cox 200A / V 2 , L 1m , W 1m and VTP 0.8, VA 100 (a) Determine the DC drain currents I D , g m and ro of MOSFET. (5 %) (b) Find the small signal voltage gain Avo vo . (5 %) vi (c) Find the small signal current gain Ais io . (5 %) ii (d) Find the input and output resistance Ro and Ri . (5 %) 2 3. (20 %) Consider the following system, sketch the Bode diagram. Vo (s) 1000s(s 50) Vi (s) (s 1)( s 20)( s 1000) 0.1 0.1 1 1 10 10 102 102 3 104 105 104 105 4-1. Consider the following ideal operational amplifier circuit. (a) Find the output function Vo f (V1 ,V2 ) .(5%) (b)What is the strategy can change the circuit to be a differential Amp. (i.e. Vo f (V1 V2 ) ) .(5%) V1 V2 Vo R1 R2 R3 R4 4-2 Consider the following Op-Amp difference amplifier. (a) Find the differential input resistance. (3%) (b) Find vo f (v1 , v2 , v3 ) (7%) R2 R1 v1 10k v2 R1 1k v3 R2 90k 4 vo 5. True and False (20 %) (a) The transfer function H ( s) s b (in the case of b>>a) sa sb represents a high-pass circuit. (b) In the Bode diagram the transition frequency signifies the voltage gain falls to 0dB, therefore we also call it the half power frequency. (c) The output signal of a differential amplifier is vo (t ) Ad (v1 v2 ) Acm vicm , in which the vicm represent the common mode input. The voltage gain Ad and Acm should be as big as possible. (d) The right side MOSFET circuit is a bad biasing scheme, since the Drain current will varying depend on the device and environment. (e) Coupling and bypass capacitors affect the high frequency characteristics of an amplifier. In general, capacitance values in the F range typically result the lower cut-off frequency in the tens of MHz range. 5 (f) The transition frequency imply the highest speed characteristic of a MOSFET . This phenomena can be modeled by two internal capacitors C gs and C gd and f T 1 . 2 (C gs C gd ) 90k 10k (g) Consider the ideal OPA amplifier circuit, the voltage gain is vi vo 90k (1 ). vi 10k vo 10k (h) Virtual short or ground is a concept based on the open-loop gain of an OPA tends to infinite. (i) According to the Miller’s theorem, z1 z(1 k ) and z 2 z /(1 k ) in which k v1 V1 Z i2 i1 i2 i1 V2 V1 Z1 Z 2 V2 v2 . (j) Use an op-amp IC (e.g. uA741) to design a voltage amplifier is much easy than others transistor amplifier, since we don’t need to trade the DC biasing problem. 6