* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Section 2 Molecules of Life Carbohydrates Carbohydrates
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
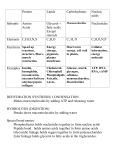
Biology Section 2 Molecules of Life Carbohydrates Carbohydrates- 1 carbon:2 hydrogen:1 oxygen Energy or structural material Monosaccharides o Monosaccharide- contains 1:2:1 of C:H:O, written as (CH2O)n where n is 3 to 8 o Glucose, fructose, and galactose are monosaccharide o Differing structure gives different properties- isomers Disaccarides and Polysaccharides o Disaccharides- two monosaccharides o Polysaccharides- three or more monosaccharides o Starch for quick energy, cellulose for structure Proteins Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen- linked amino acids Amino Acids o Carbon links hydrogen, carboxyl, amino, and R (main difference) group Dipeptides and Polypeptides o Dipeptide- two amino acids o Peptide bond- condensation reaction between amino acids o Polypeptides- long string of amino acids o Protein shape influenced by bonding, solvent, temperature Enzymes o Enzymes- RNA or protein catalysts o Physical fit between enzyme and substrate (substance being catalyzed) o Active site- folds o Slight change in shape weakens chemical bonds o Enzymes can be modified Lipids Lipids- large, nonpolar, energy-storing Fatty Acids o Fatty acid- carboxyl head, carbon chain tail o Saturated- only single bonds o Unsaturated- some double bonds Triglycerides o 3 molecules fatty acid, one molecule glycerol (alcohol) o Saturated have high melting points, unsaturated are liquid at room temperature Phospholipids o Form cell membranes due to insolubility Waxes o Long fatty-acid and alcohol chain, waterproof Steroids o Four fused carbon rings- hormones, cholesterol Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids- transfer information Biology Section 2 Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)- determines characteristics of organism Ribonucleic acid (RNA)- enzyme or makes proteins Both are polymers made of nucleotides Nucleotides- phosphate, five-carbon sugar, ring-shaped nitrogenous base