* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Biology - San Marcos Middle School
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
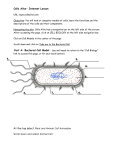
AP Biology Chapter 6 Guided Reading Assignment Name _________________________ 1. What is resolving power and why is it important in biology? 2. What is the difference between a SEM & TEM microscope? 3. Describe the purpose of cell fractionation. 4. Label the prokaryotic cell and list structure and function. 5. How do surface area and volume relate to cell size? 6. For each of the structures below note the specific structure and the function: a. Nucleus i. Nuclear envelope ii. Chromatin & Chromosomes iii. Nucleolus b. Ribosomes c. Endoplasmic reticulum i. Smooth ER ii. Rough ER d. Golgi Apparatus e. Lysosomes f. Vacuoles i. Food ii. Contractile Page 1 of 4 iii. Central g. Endomembrane system – overall h. Mitochondrion i. Plastids i. Chloroplast 1. thylakoids 2. stroma j. peroxisomes k. cytoskeleton – (include the protein that composes each type) i. microtubules 1. centrosomes and centrioles 2. cilia and flagella – include basal body ii. microfilaments 1. actin 2. myosin 3. pseudopodia iii. intermediate filaments l. Cell walls m. Extracellular matrix n. Contrast plasmodesmata, tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions. Video Review Crash Course: (you can also do a video search for “Crash Course Biology #4”) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cj8dDTHGJBY 1. What type of cell are all animal cells? What feature puts it in this category? Page 2 of 4 2. What is the function of cilia and/or flagella? What are they made of? 3. What is the function of the cell membrane (use “selective permeability” in your answer)? 4. What is the cytoplasm composed of? 5. What are the highways of the cell? What are the two types? What are their functions? 6. What are ribosomes? 7. What does the Golgi apparatus do? 8. Explain the function of lysosomes. 9. How many membranes surround the nucleus? 10. Why is the nucleus so important? 11. What is chromatin? 12. What is the function of the nucleolus? 13. Why are mitochondria so unique among organelles (hint: DNA is part of the answer)? Crash Course: (you can also do a video search for “Crash Course Biology #6”) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9UvlqAVCoqY&src_vid=cj8dDTHGJBY&feature=iv&annotation_id= annotation_919373 1. What is the function of the cell wall? What is it made of? 2. What are plastids? How are plastids similar to mitochondria? 3. What are the most important plastids? Why are they so important? 4. What is the function of the central vacuole (use the phrase “turgor pressure” in your answer)? Page 3 of 4 5. What happens to a plant when the turgor pressure is low? Bozeman Science: (you can also do a video search for “Bozeman Science Tour of the Cell”) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1Z9pqST72is 1. Why are cells small? 2. Compare and contrast optical and electron microscopes? 3. What are the monomers of proteins? 4. What are the two types of cells? What are the major differences between them? 5. What must all cells have for survival? 6. Describe each of the following: a. Nucleolus – b. Nucleus – c. Ribosome – d. Vesicle – e. Rough ER – f. Golgi Body – g. Cytoskeleton – h. Smooth ER – i. Mitochondria – j. Vacuole – k. Cytosol – l. Lysosome – m. Centriole – More information to help you study for the exam: 1) Organelles: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aczbMlSMr8U Page 4 of 4