* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Select one of your Biology instructors from another class and look
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
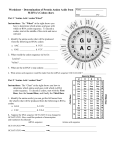
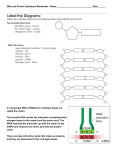
WEEK 2 PROBLEMS Problems From Chapter 8 8.1 What are the translation initiation and stop codons in the genetic code? In a random sequence of four ribonucleotides, all with equal frequency, what is the probability that any three adjacent nucleotides will be a start codon? A stop codon? In an mRNA molecule of random sequence, what is the average distance between stop codons? 8.2 If DNA consisted of only two nucleotides (say, A and T) in any sequence, what is the minimum number of adjacent nucleotides that would be needed to specify uniquely each of the 20 amino acids? 8.3 What polypeptide products are made when the alternating polymer GUGU ... is used in an in vitro protein synthesizing system that does not need a start codon? 8.4 Make a sketch of a mature eukaryotic messenger RNA molecule hybridized to the transcribed strand of DNA of a gene that contains two introns, oriented with the promoter region of the DNA at the left. Clearly label the DNA and the mRNA. Use the letters that follow to label the location and/or boundaries of each segment. Some letters may be used several times, as appropriate; and some, which are not applicable, may not be used at all. (a) 5' end (b) 3' end (c) Promoter region (d) Attenuator (e) Intron (f) Exon (g) Polyadenylation signal (h) Leader region (i) Ribosome-binding site (j) Translation start codon (k) Translation stop codon (I) 5' cap (m) Poly-A tail 8.5 Protein synthesis occurs with high fidelity. In prokaryotes, incorrect amino acids are inserted at the rate of approximately 10-3 (that is, one incorrect amino acid per 1000 translated). What is the probability that a polypeptide of 300 amino acids has exactly the amino acid sequence specified in the mRNA? For an active enzyme consisting of 4 subunits (a tetramer), each 1000 amino acids in length, what is the probability that every amino acid in every subunit was translated without error?