* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physical Property
Liquid–liquid extraction wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Colloidal crystal wikipedia , lookup
Thermomechanical analysis wikipedia , lookup
Crystallization wikipedia , lookup
Freeze-casting wikipedia , lookup
Countercurrent exchange wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Particle-size distribution wikipedia , lookup
Thermal spraying wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Glass transition wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
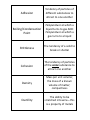
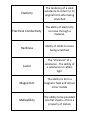
Physical Property Property that can be tested/observed without changing chemical identity of the substance; can be undone Chemical Property A property that can only be tested/observed by changing the chemical identity of a substance; hard to undo Matter Anything that has volume and mass Ability to Burn Ability of a substance to support combustion (burn) Ability to Corrode Ability of a substance to break down and form a new material when reacting with its environment—water, acid, salt, etc. Ability to Rust Ability of a metal (like iron) to bond with oxygen (from air or water) to form a new substance Adhesion Tendency of particles of different substances to attract to one another Boiling/Condensation Point Temperature at which a liquid turns to gas AND Temperature at which a gas turns to a liquid Brittleness The tendency of a solid to break or shatter Cohesion The tendency of particles of the same substance to attract one another Density Mass per unit volume; the mass of a known volume of matter; compactness Ductility The ability to be stretched into wire—this is a property of metals Elasticity The tendency of a solid substance to return to its original form after being stretched Electrical Conductivity The ability of electricity to move through a material. Hardness Ability of solids to resist being scratched Luster The “shininess” of a substance. The ability of a substance to reflect light Magnetism The ability to form a magnetic field and attract other metals Malleability The ability to be pounded into flat sheets—this is a property of metals Mass The amount of matter that something is made of. Melting/Freezing Point Temperature at which a solid turns to liquid AND Temperature at which a liquid turns to solid Solubility The ability to dissolve in another substance—how well the substance dissolves. State/phase The physical form in which a substance exists, such as a solid, liquid, gas, or plasma. Surface Tension Tendency of liquid particles to stick together, forming a “skin” Tensile Strength A measure of how far something will stretch or bend before it cracks or breaks Texture How rough or smooth a substance is Thermal Conductivity The ability to transfer thermal energy (heat) from one area to another Viscosity A liquid’s resistance to flow Volume The amount of space an object occupies