* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Glossary - Angelfire
Survey
Document related concepts
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Bremsstrahlung wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
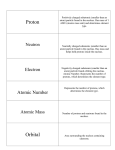
Glossary A Atom - The most basic form of an element that can exist. Atoms are made up of a positively "CHARGED" nucleus surrounded by very small and light negative electrons. The nucleus itself is made up of positive protons and neutral (uncharged) neutrons. B Beta Particle - A form of nuclear ionising radiation. It is produced when a neutron in an unstable nucleus is transformed into a proton, and emits an electron. The electron is the beta particle. They travel at around 90% of the speed of light and are stopped by a few mm of aluminium. Black Hole - A region of space that has gravity so strong that not even light can escape from it. Anything entering a black hole is lost forever. The edge of a black hole is called the "event horizon", and this is the part you mustn't cross. Although black holes are strictly speaking still a theory, there is strong evidence to support their existence. It is thought that black holes exist at the centre of some galaxies, and inside "QUASARS" Blue-shift - When an object is moving towards us very quickly, the light waves coming from it become compressed, so that when they reach us they are of shorter wavelength (and higher frequency) than when first emitted. Catalyst - A chemical substance that helps to speed up a chemical reaction Charge - Charge is a property of an electron (-), a proton (+) and many other "SUBATOMIC PARTICLES". The unit of charge is the COULOMB (C). The charge on one electron is VERY small; -1.6 E-19 C (0.00000000000000000016C). Moving charge results in an electric "CURRENT". D Diffusion - Movement of molecules from a place of high concentration to a place of low concentration. Dielectric - The non conducting layer separating two plates in a capacitor. The properties of the dielectric govern the maximum working voltage of the capacitor and the capacitance of the capacitor. E Electron - "FUNDAMENTAL PARTICLE" with negative charge. One of a group of particles called "LEPTONS", it has a charge of -1.6 E-19 C (0.00000000000000000016 C) and a mass of 1/1860 u. Energy - this is the capacity for doing work. Whenever anything is done, energy is involved, being converted from one form to another. There are many types of energy, such as Gravitational potential, Elastic potential, Electrical potential, Heat, Light, Kinetic (movement), Nuclear, Chemical potential. In any energy conversion, the TOTAL energy is always conserved. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but is converted from one form to another - the Principle of Conservation of Energy. Equilibrium - There are different types of equilibrium (eqm), such as chemical eqm. In physics we normally work with mechanical eqm. A system is in equilibrium if i) the total "FORCE" acting in any direction is zero, and ii) the total "MOMENT" about any point is zero. F Force - An entity which may cause acceleration, deformation, rotation, sheering etc. A force is a push or a pull. The unit of force is the newton (N). Examples of forces are weight (caused by gravity), friction and tension. Fundamental Particle - One of the most basic building blocks of matter. These particles cannot be broken down any further (as far as we know!). Electrons and Quarks (Which make up protons and neutrons) are examples of fundamental particles G Gamma Radiation - A high energy form of electromagnetic radiation. It is emitted from a nucleus, usually after the nucleus has undergone an alpha or beta decay. It is weakly ionising, it has no charge and it has no mass. Gamma rays are reduced by thick lead, steel and concrete. Galaxy - A huge collection of around 100 000 000 000 "STARS" (One hundred thousand million, or one hundred billion). A galaxy may be spiral, elliptical or irregular. We inhabit a spiral galaxy called the "milky way". H Haemoglobin Iron - containing pigment that carries oxygen in the blood. Hormone - A protein molecule that is secreted from a gland into the blood. It changes the function of other cells around the body. Hydrotropism - Growth of a plant in response to the presence of water. I Isotope - Isotopes of the same element have the same number of "PROTONS" but different numbers of "NEUTRONS". If two atoms have different numbers of protons then they must also have different numbers of electrons in order to be electrically neutral. They therefore have different chemical properties and are atoms of different elements altogether. J Joule (J) - The unit of energy. 1 joule is the kinetic energy of a mass of 1kg moving at 1m/s. 4200J of heat energy is required to raise the temperature of 1kg of water by 1 deg. Celcius. K Kelvin - Named after Lord Kelvin, this is also called the absolute temperature scale. The interval of 1 Kelvin (1K) is equal to 1 degree Celcius. Absolute zero (0K) is -273.15 deg. Celcius. To convert a temperature in deg. Celcius into Kelvin, add 273.15. L Light - Pure electromagnetic energy. It may or may not be visible. See "ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM" M Mass - The amount of matter an object contains. The unit of mass is the Kilogram. Note that mass is not the same as "WEIGHT". Weight is a force, and so has the units "newton". Momentum - NOT TO BE CONFUSED WITH MOMENT, this is a quantity which something has because of its motion. MOMENTUM (kgm/s)= MASS(kg) x VELOCITY(m/s). N Nucleus - The control centre of plant and animal cells which contains the genetic information. Nucleus - The tiny central part of an atom, occupying little space but carrying almost all of the mass of the atom. Made up of protons and neutrons Neutral - Without electric charge Neutron - A neutral particle in the nucleus of an atom. It is made up of three quarks (dud). During a beta decay, the neutron is converted to a proton and an electron is emitted. The electron is the beta particle O Optimum - The conditions (temperature, pH, etc.) at which the enzyme works best P pH - A scale from 1 (acid) to 14 (alkaline) that measures acidity and alkalinity Product - The chemical molecules left at the end of a reaction Q Quark - A fundamental particle. There are 6 known types of quark (UP, DOWN, STRANGE, CHARM, TOP, BOTTOM) although all the nuclear matter in the known universe is made up of UP and DOWN. Quarks exist in triplets (a proton is made up of UP, UP, DOWN) or Quark-Antiquark pairs (see "ANTIMATTER"). R Radiation- Radiation is a form of energy that emitted from some chemical process. It contains of wavelength, frequency. S Scalar - Scalar quantities only have size (also called magnitude). They do not need to have a specified direction. Examples of scalars are "SPEED", "MASS", "ENERGY", "TEMPERATURE". T Temperature - How hot something is, measured in degrees Celcius or Kelvin. It is NOT the same as heat, which is a form of energy, measured in joule. To illustrate this, consider a spark and a kettle of boiling water. The spark may be at several hundred degrees celcius, but will harm you less than a kettle full of water at only 100 deg. celcius. This is because the water contains more heat energy in total. U Ultrasound - Sound which is at a "FREQUENCY" higher than can be heard by the human ear is called ultrasound. It displays all the usual wave properties, such as reflection, refraction and diffraction, and has many uses. Typical examples are monitoring unborn children, monitoring blood flow and echo-sounding. In echo-sounding, pulses of ultrasound are reflected off the seabed or off shoals of fish and the time taken to receive the reflection is used to calculate depth. V Vector - A quantity which has size (also called magnitude) and direction. (As opposed to a "SCALAR" which only has size). Examples of vectors are "FORCE", "VELOCITY", "ACCELERATION", "WEIGHT", "DISPLACEMENT W Wavelength - The distance between two troughs or two peaks on a wave. Weight - This is the "FORCE" with which something is attracted to the Earth. Weight (N)= mass(kg) x gravitational field strength(N/kg). X X-ray - Part of the electromagnetic spectrum. X-rays travel through some materials but not others, and they show up on photographic film. These properties make them ideal for medical uses, such as scanning for broken bones. Over exposure to X-rays can be dangerous, and so people who work with them all the time use screens to shield them from the rays.