* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Biology - HPHSAPBIO
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
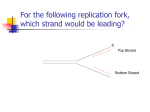
AP Biology Objectives Chapter 16 / Chapter 17 DNA as the Genetic Material 1. Summarize the experiments performed by the following scientists that provided evidence that DNA is the genetic material: a. Frederick Griffith b. Oswald Avery, Maclyn McCarty, and Colin MacLeod c. Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase d. Erwin Chargaff 2. Explain how Watson and Crick deduced the structure of DNA and describe the evidence they used. Explain the significance of the research of Rosalind Franklin. 3. Describe the structure of DNA. Explain the "base-pairing rule" and describe its significance. DNA Replication and Repair 4. Describe the semiconservative model of replication and the significance of the experiments by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl. 5. Describe the process of DNA replication. Note the structure of the many origins of replication and replication forks and explain the role of DNA polymerase. 6. Define "antiparallel" and explain why continuous synthesis of both DNA strands is not possible. 7. Distinguish between the leading strand and the lagging strand. 8. Explain how the lagging strand is synthesized even though DNA polymerase can add nucleotides only to the 3' end. 9. Explain the roles of DNA ligase, primer, primase, helicase, and the single-strand binding protein. 10. Explain why an analogy can be made comparing DNA replication to a locomotive made of DNA polymerase moving along a railroad track of DNA. Evolution, Unity, and Diversity 11. Explain the roles of DNA polymerase, mismatch repair enzymes, and nuclease in DNA proofreading and repair. 12. Describe the structure and functions of telomeres. Explain the significance of telomerase to healthy and cancerous cells. The Connection between Genes and Proteins 13. Explain how RNA differs from DNA. 14. Briefly explain the central dogma of protein synthesis 15. Distinguish between transcription and translation. 16. Compare where transcription and translation occur in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes. 17. Define "codon" and explain the relationship between the linear sequence of codons on mRNA and the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide. 18. Explain why polypeptides begin with methionine when they are synthesized. 19. Explain in what way the genetic code is redundant and unambiguous. 20. Explain the significance of the reading frame during translation. 21. Explain the evolutionary significance of a nearly universal genetic code. The Synthesis and Processing of RNA 22. Explain how RNA polymerase recognizes where transcription should begin. Describe the promoter, the terminator, and the transcription unit. 23. Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 24. Explain how RNA is modified after transcription in eukaryotic cells. 25. Define and explain the role of ribozymes. 26. Describe the functional and evolutionary significance of introns. The Synthesis of Protein 27. Describe the structure and functions of tRNA. 28. Describe the structure and functions of ribosomes. 29. Describe the process of translation (including initiation, elongation, and termination) and explain which enzymes, protein factors, and energy sources are needed for each stage. 30. Describe the significance of polyribosomes. 31. Explain what determines the primary structure of a protein and describe how a polypeptide must be modified before it becomes fully functional. 32. Describe what determines whether a ribosome will be free in the cytosol or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. 33. Compare protein synthesis in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 34. Define "point mutations." Distinguish between base-pair substitutions and base-pair insertions. Give examples of each and note the significance of such changes. 35. Describe several examples of mutagens and explain how they cause mutations. .