* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide for Genetics Test
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
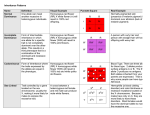
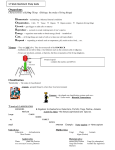
Study Guide for Genetics Test Please answer the following questions on your own sheet of paper or index cards. If the question asks you to do something, please do that on your own sheet of paper as well. Hint: You will need to make punnett squares for some!! 1. What type of plants resulted when Mendel crossed purebred tall and purebred short plants together? What were the genotypic and phenotypic ratios? 2. What is a hybrid? 3. What word refers to the physical characteristics that are studied in genetics? 4. What does a punnett square show you? 5. What does phenotype mean? 6. What does genotype mean? 7. Using the letters T and t write out Homozygous dominant, Homozygous recessive, and heterozygous and label each one with what it is. 8. What are the factors that control traits called? 9. What are the different forms of genes called? 10. Explain to me what it means to be homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive and/or heterozygous. 11. An organism that has 2 identical alleles for a trait is known as what? 12. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? 13. What combination of chromosomes will result in a male / a female? 14. When sex cells combine during fertilization each sex cells contributes _________ the number of normal chromosomes. 15. What makes a person a carrier? Who can only be carriers males or females? why? 16. Tell me what a pedigree is and draw an example of one. 17. What is hemophilia? How is it caused? 18. What is probability? 19. What is genetics? 20. What is heredity? 21. What is hybridization? 22. What's the difference between Asexual and Sexual reproduction? 23. What types of things use Asexual reproduction? 24. What types of things use sexual reproduction? 25. What are the 4 bases in DNA? 26. What are the rungs of the DNA ladder made of? 27. What are the sides of the DNA ladder composed of? Answers to Genetics Study Guide 1. Genotype = 100%Tt. Phenotype = 100% tall 2. An organism that has two different alleles for a trait. 3. Traits 4. It shows all the possible combinations of alleles 5. An organisms physical appearance 6. An organisms genetic makeup 7. Homozygous dominant – TT. Homozygous recessive — tt. Heterozygous - Tt 8. genes 9. alleles 10. Homozygous dominant have 2 dominant alleles (TT). Homozygous recessive has two recessive alleles (tt). Heterozygous has one dominant and one recessive allele (Tt). 11. Purebred 12. Genes are carried from parents to offspring on chromosomes 13. Male XY female-XX 14. half (which is 23) 15. A person who has one allele for a trait but does not exhibit the trait in their phenotype. Females can only be carriers because they have 2 X chromosomes, and if a male has one allele for the disease then they are not carriers, they actually have the disease. 16. A chart that tracks which members of a family have a particular trait 17. when a person’s blood clots very slowly or not at all due to the inheritance of a recessive allele 18. The likelihood that a possible future event will occur in any given instance of the event. 19. The scientific study of heredity. 20. The passing of genetic traits from parent to offspring. 21. A selective breeding method in which two genetically different individuals are crossed 22. Sexual involves 2 parents and results in genetic variation, Asexual involves one parent and generally makes offspring that are genetically similar to the parent 23. Bacteria, some plants, hydra, coral 24. Humans, Plants, most animals, etc... 25. Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G) 26. A pair of bases 27. Sugar (Deoxyribose) and Phosphate