* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam Review Formula Sheet
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
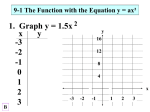
Exam Review Sheet Grade 11 Functions and Applications MCF3M1 Introduction to Functions Function Notation A function is like a machine. When an x-value in the domain of the function f enters, the machine produces the output f (x) . The output f (x) is determined by the rule of the function. Vertical Line TestEx 1) Which are functions: a) b) c) d) x -1 0 1 2 y y 1 2 x x -2 -2 2 -2 -2 Ex 2) If g(x) = 2x2 + 3, evaluate when x = 4. Expanding Expand: a) 2 x 1 x 2 b) 3 x 1 3 x 1 Factoring a) x x 20 2 2 b) 2 x 2 x 24 2 c) 3 x 11 x 14 y 5 5 5 5 Domain and Range Number System Symbol Natural Numbers Description The natural numbers start at 1 and increase by one to infinity. For example: 1, 2,3, 4, Whole Numbers W The whole numbers start at 0 and increase by one to infinity. For example: 0,1, 2,3, 4, Integers Z The integers are consist of all the positive natural numbers, their negatives and the number zero. The set of integers start at 0 and increase by one in one direction to infinity, and decrease by one in the other direction to negative infinity. For example , 4, 3, 2, 1, 0,1, 2,3, 4, The symbol Z is used to represent the set of integer numbers. The German word for numbers is Zahlen hence the usage of the symbol Z . Real Numbers R The real numbers are the set of all positive and negative integers, fractions and irrational numbers (numbers that have decimal parts that do not terminate or repeat) Domain – Range – Ex) State the domain and range of each of the following: Exam Review Sheet Grade 11 Functions and Applications MCF3M1 Quadratics Investigating Quadratic Functions Complete the table below and graph the data. Label the following words on your graph: axis of symmetry, zeros, x-intercept, vertex, minimum/maximum value. x y -2 12 -1 5 0 0 1 -3 2 -4 3 -3 First Differences Second Differences Vertex Form y = a (x – h)2 + k Graph the following by using the vertex and step Example: Graph the following equation: y = -3(x – 4)2 + 5 Vertex: Optimal (Max/Min) Value: Axis of Symmetry: Step: Factored Form y = a (x – s) (x – t) Sketch the graph of the following equation by filling out the table below: y = -2x2 – 4x + 16 Zeros: Step: Axis of Symmetry: Optimal (Max/Min) Value: Vertex: Application 1. An outdoor gear company models the profit on its newest backpack using the function , where x is the number of backpacks, in thousands, that the company produces and P(x) is the profit, in tens of thousands of dollars. a. What is the break even point for the backpacks (where does the company make ZERO profit)? [2] b. What is the maximum profit the company can earn from the backpacks? [3] c. What is the y-intercept of the profit function? Explain the meaning of this value in the context of the question. 2. Find the equation for the data in all three forms. How far are you from the CBR at 3.25 seconds? Time (s) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 Distance from Motion Detector (m) 0 8.75 15 18.75 20 18.75 15 8.75 0 Exam Review Sheet Grade 11 Functions and Applications MCF3M1 Quadratics 2 – Completing the Square Introduction Problem You throw a paper airplane from a height of 4 m above the ground. The height of the airplane as a function of time is modeled by the function: h(t) = t2 + 10t + 4. Find the maximum height of the airplane Completing the Square Using Tiles Can we convert the following into vertex form by factoring? y = x2 + 10x + 4 h = ______________________ k = ______________________ Completing the Square Using Algebra Find the minimum of the following: y = -2x2 – 16x + 3 I. Remove the common factor (the a-value) on both variable terms II. Find the constant that must be added and subtracted to make a perfect square. Divide the number on the x-term by 2, and square it. COMPLETE THE SQUARE! III. Rewrite the expression by adding, then subtracting, this value after the x-term inside the brackets. IV. Group the three terms that form the perfect square. Move the subtracted value outside the brackets by multiplying it by the common constant factor (a-value). V. Factor the perfect square and collect like terms. The Quadratic Formula A diver dives from a cliff at a height of 14 m above the sea. The height of the diver above the sea at time t in seconds for the dive can be modeled by the function: h(t) = 2x2 – 12x + 14 Find the time when the diver hits the water. Solve using two methods. x b b 2 4ac 2a Behaviour At Roots If b 2 4ac is positive, there are two different real roots. If b 2 4ac is zero, there are two equal real roots If b 2 4ac is negative, there are no real roots. Ex) Determine the nature of the roots of these equations: x2 9 x 7 0 4 x 2 36 x 81 0 Determining An Equation From A Graph Find the equation for the quadratic below in (i) vertex, (ii) standard and (iii) factored form Exam Review Sheet Grade 11 Functions and Applications MCF3M1 Trigonometry Right Triangle Trigonometry B Pythagorean Theorem a2 + b2 = c2 Trigonometric Ratios (SOH CAH TOA) sin A=OPP cos A = ADJ tan A = OPP HYP HYP ADJ c a C for example to find an angle from sin A = OPP/HYP A = sin-1(OPP/HYP) A b Non Right Triangle Trigonometry C a a b A Sine Law c sin A B Which Path to Choose? b sin B c sin C Cosine Law a 2 b 2 c 2 2bc cos A Examples Triangle B What Law? Pythagorean Theorem | SOH CAH TOA | Sine Law | Cosine Law If I was finding the length of side a, I would use 25 cm a ________________________________ 20° A 40 cm C P If I was finding the length of side p, I would use ________________________________ 124 74 Q R p If I was finding the length of side x, I would use ________________________________ M If I was finding the value of angle K, I would use 83 ________________________________ L 74 110 K Exam Review Sheet Grade 11 Functions and Applications MCF3M1 Trigonometric Functions Period Functions Draw the graph of the walk on the grid provided below: CBR 1m Hula-Hoop Modeling the Sine Function Draw the graph of y = sin(x) on the grid provided below: Transformations of y = sin(x) y a sin( x c) d Ex) Graph the following: y = 2 sin(x – 60o) – 3 Ex) Find TWO possible equations for the graph below. Equation 1: Equation 2: What are the transformations that have happened to this sine graph? Exam Review Sheet Grade 11 Functions and Applications MCF3M1 Exponential Functions Identifying Models: Linear, Quadratic and Exponential Identify the type of model the data fits. x 1 y First Differen Second ces Differen 1 ces x 1 y First Differe Second 0 nces Differen ces x 0 y First Differe Second 2 nces Differen ces 2 3 2 1 1 4 3 5 3 4 2 8 4 7 4 9 3 16 5 9 5 16 4 32 Graphs of Exponential Functions Exponential Growth Exponential Decay Exponential Growth and Decay Problems Ex 1) A new form of bacteria doubles in population every 20 minutes. Initially there were 3 bacteria. a. Write an equation to represent this problem. b. Use your equation to find the number of bacteria after 10 hours. Ex 2) You have invested $1000 in the bank. The bank pays you 3.4% of interest per year. c. Write an equation to determine the amount of money in your account after x years d. How much money will you have in the bank after 15 years? Ex 3) The half-life of radioactive radium is 7 days. If you originally had 224 mg of this radioactive substance, how much would be present after one week? Laws of Exponents Law Example x1 = x 61 = 6 x0 = 1 70 = 1 x-1 = 1/x 4-1 = 1/4 xmxn = xm+n x2x3 = x2+3 = x5 xm/xn = xm-n x4/x2 = x4-2 = x2 (xm)n = xmn (x2)3 = x2×3 = x6 (xy)n = xnyn (x2y)3 = x6y3 (x/y)n = xn/yn (x/y)2 = x2 / y2 x-n = 1/xn x-3 = 1/x3 1/x-n = xn 1/x-3 = x3 Exam Review Sheet Grade 11 Functions and Applications MCF3M1 Financial Mathematics Simple Interest I = Prt IInterest Earned PPrinciple rInterest Rate in decimal (i.e. 4%=0.04) tThe length of the investment in years (i.e.36 months, t=3) Compound Interest A = P(1 + i)n or P = A(1 + i)–n A=FV=Amount or FV P=PV=Present Value (What you put down today. This value is “-“ on the graphing calculator) i=interest rate per compound period (i.e. 4%/a compounded monthly: i=0.04/12) n=number of compounds total (i.e. you invest for 3 years compounded semi-annually: n=3x2=6compounds) Compound Interest using the TVM Solver Press Menu8:Finance1:Finance Solver Time in years multiplied by compounding periods Interest rate in percent as stated in question Present Value (value is Negative if money is given) PMT stays 0 Future Value P/Y Compounds per Year C/Y Compounds per Year Annuities using the TVM Solver Press Menu8:Finance1:Finance Solver Total Number of Compounds Interest rate in percent as stated in question Present Value (value is Negative if money is given) PMT-Payment per compound period Future Value P/Y Payments per Year C/Y Compounds per Year Quadratics