* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download OBJECTIVES: Students will gain an understanding of how
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
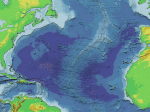
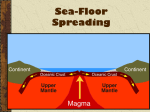
Honors Earth/Space Science Name _________________________________ SEAFLOOR SPREADING IN THE ATLANTIC OCEAN Period _______ Date ______________ OBJECTIVES: Students will… Observe and analyze the ages of seafloor rocks. Identify the Mid-Atlantic Spreading Ridge (MAR). Use map scales to determine the distance between the MAR and adjacent coastlines. Determine rates of sea floor spreading between two tectonic plates. MODEL 1: Strip map of a portion of the North Atlantic region between North America and Africa. The coastlines are given a heavy line and the continental shelf edge is a lighter outline. Seafloor basalt ages are indicated in millions of years. Basalt is the type of rock that is found in the ocean floor (crust). It is igneous. The numbers indicate the age of the sea floor rocks in millions of years. MODEL 2: Below is a profile (side-view) of the elevation of the seafloor between Points A and B with the 0year old basalts indicated. These new basalts are associated with active submarine volcanoes. Point A Point B Age = 0 years USING OBSERVATIONS TO GENERATE A HYPOTHESIS… 1. What continents are shown in Model 1? 2. List three observations of the distribution of basalt ages: 3. Develop a statement describing the distribution of basalt ages: 4. List three observations about the elevation of the seafloor: 5. Develop a statement describing the elevation of the seafloor: Scientists refer to the Mid-Atlantic submarine mountainous region as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The Theory of Seafloor Spreading states that seafloor spreading is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new ocean crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. Seafloor spreading helps explain the theory of continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics. When oceanic plates diverge, tensional stress causes fractures to occur in the lithosphere. Basaltic magma rises up the fractures and cools on the ocean floor to form new sea floor. Older rocks will be found further away from the spreading zone while younger rocks will be found nearer to the spreading zone. USING OBSERVATIONS TO MAKE CALCULATIONS… 6. Creating a scale for the map in Model 1. a. Using Model 2, determine the actual distance between Points A and B. Record the value in kilometers: b. Use a ruler to draw a line between Points A and B on the map in Model 1. Measure and record that distance in centimeters: c. Determine the scale of the map by simplifying the ratio of the map distance/actual distance (1 cm = ________km): 7. Find the rate of movement between the spreading ridge and Point A. a. Using the scale of the map that you determined in question 6, find and record the distance between Point A and the mid-ocean ridge in km: b. Record the age of the seafloor basalts nearest to Point A: c. Determine the rate or velocity that Point A moved away from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge in i. ____________________km per MY ii. ____________________cm per year This rate is actually considered the “half-rate” of seafloor spreading because Africa is also moving away from the ridge. The actual rate of seafloor spreading is determined by calculating the rates on both sides of the ridge and adding them together. 8. Find the rate of movement between the spreading ridge and Point B. a. Using the scale of the map that you determined in question 8, find and record the distance between Point B and the mid-ocean ridge in km: b. Record the age of the seafloor basalts nearest to Point B: c. Determine the rate or velocity that Point B moved away from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge in i. ____________________km per MY ii. ____________________cm per year 9. Analyze and compare your answers in questions 7 and 8. Write a statement about how the rates are similar and how they are different: 10. How much has the distance (in cm) between North America and Africa increased since you were born? 11. How much does the distance (in meters) increase during the average lifetime of an American (~82 years)? 12. How much closer (in meters) were these two continents when Columbus made his voyages (in 1492)?