* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6th Grade Math Lesson Plans - d
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
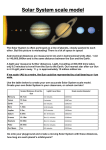
Lesson Component Standard: 1. Physical Science Observe, explain, and predict natural phenomena governed by Newton's laws of motion, acknowledging the limitations of their application to very small or very fast objects Standard: 3. Earth Systems Science: 3. The solar system is a. Construct a scale model of the solar system, and use it to explain the motion of objects in the system such a planets, comprised of various objects that orbit the Sun and are Sun, Moons, asteroids, comets, and dwarf planets (DOK 2- classified based on their characteristics 4. The relative 3) positions and motions of Earth, Moon, and Sun can be b. Describe methods and equipment used to explore the solar used to explain observable effects such as seasons, system and beyond (DOK 1) eclipses, and Moon phases c. Design an investigation that involves direct observation of e. f. Learning Target: Student “I Can…” statement Questions Varied, high quality, DOK 2,3 that will be used Written prior to lesson Friday 12/21 Standard: 3. Earth Systems Science: The solar system is comprised of various objects that orbit the Sun and are classified based on their characteristics Students can: d. Objective Teacher Centered Using action Verbs Bloom’s Hess Bell Marzano Thursday 12/20 objects in the sky, and analyze and explain results (DOK 24) Research, critique, and communicate scientific theories that explain how the solar system was formed (DOK 1-3) Use computer data sets and simulations to explore objects in the solar system (DOK 1-2) Recognize that mathematical models are used to predict orbital paths and events Students will create a poster for their rockets. I can create a poster for my rocket. Students will use their calculations of planet size and distances to make a scale model of the solar system Celebration of PBL and Mission to Mar Field trip. Students will analyze key elements of the Apollo 13 mission and apply them to [1] what they have learned and experienced so far in science; and [2] relate them to current events. I can create a scale model of the solar system using my calculations. I can use my knowledge about Newton’s Laws of Motion, and Team work to explain various scenes in the movie Apollo 13. If you could make a solar system model that could take over the entire school land area what scale would you use? * Why is it important to “ground” someone if it is suspected they were exposed to the measles? * What could happen if the astronauts were allowed to have physical contact with their families just prior to their mission? * How is the vestibular system (what we learned from our Mission to Mars) affected by microgravity? Explain. * Discuss the importance of 21st Century Skills: effective communicator, collaboration, active tem participant in the success of Apollo 13. * How can we prevent the desensitization of the public with the media? Can the media go to far (or not far enough)? No Students Standard(s) Number of Standard Kid Friendly Language Monday 12/17 Lesson Plans Week of December 17, 2012 Tuesday Wednesday 12/18 12/19 Strategies/Activities: Review Rocket project Hook to prior learning or Anticipatory Set: Design a poster to sell their rocket at an exhibit Do now: Why would we use two different scales when creating of model of the solar system? Modeling I Do, We Do, You Do Frequent check for progress toward Mastery Creation of poster Discussion: Different scales Create a model of the solar system using the calculations. Closure/Student Reflection Assessments/Check for Mastery: Frequent Formative How will you know they know? What will you do if they do or don’t demonstrate mastery? Varied Learning Abilities What are you doing to address the unique needs of students Key Vocabulary Terms Poster Entrance Ticket: Students will list all the skills that were important during their PBL and Mission to Mars During the activity: Students will respond to questions posed by teacher individually and after discussing with a shoulder partner. Exit Ticket: Students will synthesize a “mission statement” that will identify at least 3 21st Century skills that are vital in the success of a stressful mission (tie in what they learned from the PBL/Challenger Learning Center with what the astronauts/Mission Control handled in Apollo 13) Solar system model Exit ticket Students who struggle can be grouped with more advanced students. Scale Astronomical unit Scale factor Proximity Sentence frames to facilitate thoughtful answers Gravity Newton’s laws of Motion 21st Century skills