* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lessons 1-5, 9-10 study guide 2014 (answer key).
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
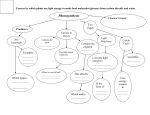
Lessons 1-5, 7 Test Study Guide ANSWER KEY Review Questions: 1. What is an organism? A living thing that goes through the 5 life processes 2. What are the 5 traits of life? Reproduction, Response, Movement, Growth, Death 3. What is the order of classification of plants and animals? (Kingdom, Phylum…etc.) Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order Family, Genus, Species 4. How do we get the scientific name of an organism? (by what two parts in classification)? Genus, Species Lesson 2- WOWBugs Review Questions: 1. Review the 10 scientific drawing rules from your comp. book. 2. The study of which insect laid the groundwork for modern genetics? Fruit Fly 3. What do all insects have in common? 3 part body (head, Thorax, Abdomen), 6 legs, 4 wings, exoskeleton 4. How have some insects caused humans trouble destroy crops, transmit disease 5. How have some insects helped humans Pollinate, destroy pest populations 6. Define entomologist A scientist who studies insects 7. Look at the diagram on p. 25. How does the dorsal view and lateral view differ? You can see different things Lesson 3- Worms Review Questions: 1. Be able to label a diagram of the blackworm and earthworm. Esophagus Crop hearts Gizzard mouth clitellum ventral blood vessel dorsal blood vessel segments intestine anus 2. Describe what you learned about the pulse rate of a blackworm at the anterior vs. posterior sides. They are different 3. Describe the similarities and differences of the earthworm and blackworm. BACKWARDS!!! Blackworm Both Earthworm 2 “hearts” (dorsal and ventral blood vessels) tail end is for gas exchange (sticks p. end out) body reproduces by fragmentation location) Lives in water similar shape segmented tiny hairs Multiple “Hearts” Gas exchange with the whole Clitellum (all body parts in one Move by contracting muscles Larger Regeneration Lives in soil Hermaphrodite (both male and female) Lesson 4- Ponds Review Questions: 1. What are living components to your pond? Rice, lemna, organisms (hay, leaf all once living) 2. What are non-living components to your pond? Soil, water, rocks 3. Define: a. Ecosystem- AN AREA WHERE LIVING AND NON-LIVING THINGS INTERACT. b. Habitat- The place where organism’s needs are met. c. Niche- The function of the organism in an ecosystem. Lesson 5- Plants Review Questions: 1. What are the 5 characteristics that you use to determine if a plant is a monocot or dicot? Leaves, roots, seeds, stems, flower parts 2. What is transpiration? When water vapor leaves the leaf when the stomata are formed. (process of water loss from the leaves.) 3. A simple form of sugar is called glucose which is the only the only, one type of) food for plants because it gives the plant energy. Lesson 9: Flowering Plants: Review Questions: 1. What is the structure you see below? OVARY Label the parts. OVARY EGG 2. Label this diagram of a perfect flower: PETALS STAMEN ANTHER FILAMENT STIGMA STYLE OVARY PISTIL Lesson 10 Review Questions: 3. Label this leaf: VEIN BLADE PETIOLE 4. Draw and label a stoma that is open and one that is closed. During what time of the day are they usually opened and closed? DAY Open (during______________) Closed (at NIGHT _____________) 5. What are stoma and how are stoma formed? Tiny openings in leaves. 5 6. Describe guard cells. A pair of sausage shaped cells that open and close to help the leaf absorb and get rid of water. 7. What is transpiration? When water vapor leaves the leaf when the stomata are formed. (process of water loss from the leaves.) 8. What is most responsible for the oxygen in our atmosphere? Plants and algae 9. Define: a. Pistle- female reproductive structure on a flower b. Stamen- male reproductive structure on a flower c. Anther- contains the pollen d. Filament- holds the anther e. Ovary- Contains the eggs. f. Stigma- Contains sticky substances so that the pollen can be collected. g. Style- Carries the pollen nuclei down to the ovary. h. Blade- flat part of the leaf i. Vein- transports materials through the leaf j. Petiole- holds the leaf to the stem k. Xylem- transports Water, minerals and nutrients. l. Phloem- transports food (glucose) to the rest of the plant. m. Photosynthesis- process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy Carbon Dioxide + Sunlight + Water Oxygen + Glucose (inputs) (outputs) 6