* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Worksheet 4
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
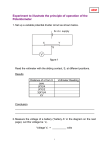
Worksheet 4 Series and Parallel Circuits using bulbs, batteries, wires and meters Engage: Show students two different strings of holiday lights: one strand has lights that go out when one light bulb is removed and another has lights that stay on when one bulb is removed. Students will be given: 1.5-V batteries, several holiday lights (recycled and cut from and old strand), conducting wires with alligator clip ends Explore: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Connect your bulbs to the batteries so that when one bulb is disconnected the whole strand of lights goes out. This is a series circuit. Draw your circuit by using standard symbols. Use your voltmeter to measure the voltage of the batteries. RECORD Use your voltmeter to measure the voltage across each bulb. RECORD What do you notice about the total voltage from the battery compared to the sum of the voltages from each bulb? Now use your ammeter to measure the current going through each bulb. RECORD. SERIES CIRCUIT Voltage Batteries Bulb 1 Bulb 2 Bulb 3 Current 7. 8. Connect your bulbs to the batteries so that when one bulb is disconnected the whole strand of lights does NOT go out. This is a parallel circuit. Draw your circuit by using standard symbols. 9. 10. 11. Use your voltmeter to measure the voltage of the batteries. RECORD Use your voltmeter to measure the voltage across each bulb. RECORD Now use your ammeter to measure the current across each bulb. RECORD PARALLEL CIRCUIT Voltage Current Batteries Bulb 1 Bulb 2 Bulb 3 EXTEND and ELABORATE 1. In our classroom explain whether the lights are connected in series or in parallel. How do you know? 2. Which type of holiday lights would you rather purchase: series lights or parallel lights? Why? 3. Return to your experiment with the bulb, batteries and wires. Starting with one bulb, add more bulbs and describe what happens to the brightness as you add additional bulbs in series. 4 With the bulbs, batteries and wires start with one bulb and add more bulbs in parallel. Describe what happens to the brightness as you add additional bulbs. Discussion Guide – the differences between the real world circuits and the circuit simulations 1. For you, what were the best parts of using the computer simulation? 2. Which setup (real vs. computer) allowed you to make changes in your circuit easier? 3. Which setup (real vs. computer) would be better to use if you were about to wire a house? 4. What differences did you notice between the outcomes of the two setups? 5. What recommendations would you make to someone using each of these setups next year? Worksheet 4 See possible student responses in RED Series and Parallel Circuits using bulbs, batteries, wires and meters Engage: Show students two different strings of holiday lights: one strand has lights that go out when one light bulb is removed and another has lights that stay on when one bulb is removed. Students will be given: 1.5-V batteries, several holiday lights (recycled and cut from and old strand), conducting wires with alligator clip ends Explore: 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. Connect your bulbs to the batteries so that when one bulb is disconnected the whole strand of lights goes out. This is a series circuit. Draw your circuit by using standard symbols. Use your voltmeter to measure the voltage of the batteries. RECORD Use your voltmeter to measure the voltage across each bulb. RECORD What do you notice about the total voltage from the battery compared to the sum of the voltages from each bulb? Now use your ammeter to measure the current going through each bulb. RECORD. SERIES CIRCUIT Voltage Batteries Bulb 1 Bulb 2 Bulb 3 Current 18. 19. Connect your bulbs to the batteries so that when one bulb is disconnected the whole strand of lights does NOT go out. This is a parallel circuit. Draw your circuit by using standard symbols. 20. 21. 22. Use your voltmeter to measure the voltage of the batteries. RECORD Use your voltmeter to measure the voltage across each bulb. RECORD Now use your ammeter to measure the current across each bulb. RECORD PARALLEL CIRCUIT Voltage Current Batteries Bulb 1 Bulb 2 Bulb 3 EXTEND and ELABORATE 4. In our classroom explain whether the lights are connected in series or in parallel. How do you know? Should indicate “parallel” because one can go out but this does not affect the others 5. Which type of holiday lights would you rather purchase: series lights or parallel lights? Why? May say “series” because of lowered cost, may indicate “parallel” because of the tendency of the other lights to stay lit. 6. Return to your experiment with the bulb, batteries and wires. Starting with one bulb, add more bulbs and describe what happens to the brightness as you add additional bulbs in series. Addition of more bulbs causes them to get dimmer 7. With the bulbs, batteries and wires start with one bulb and add more bulbs in parallel. Describe what happens to the brightness as you add additional bulbs. Addition of more bulbs causes them to get brighter