* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Question 5 - Dominican
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
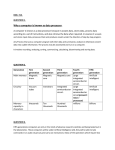
Fifth Year Physics Summer 2005 STUDENT NAME: Percentage Dominican College 5th Year Summer Examinations, 2005 Physics (200 marks) Teacher: Mr. M. Moriarty Time: 2 hours Attempt two experiment and two long questions. Each experiment question carries 40 marks and each long question carries 60 marks. Answers and supporting work should be written into the boxes provided. Graph paper is available, if needed. The symbol indicates that supporting work must be shown to obtain full marks. Make and model of calculator used: For the Examiner’s use only: Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total Grade Page 1 of 12 Mark Fifth Year Physics Summer 2005 Question 1 A student performs an experiment to determine the focal length of a converging lens using a lamp box and a screen. She measured the distance between the lamp box and the lens and the distance between the lens and the image and obtained the following results: u/cm v/cm 12 61 16 26.7 20 21 24 17.2 28 15.4 30 15.0 Plot a suitable graph and use it to find the focal length of the converging lens. (16) Using two data pairs in the table above, calculate two estimates for the focal length of the lens. (12) Compare the values you have found for the focal length using the graph and using the relationship formula. Which do you think is the more accurate result? (12) Page 2 of 12 Fifth Year Physics Summer 2005 Question 2 The following is part of a student’s account of an experiment to measure the specific latent heat of vaporization of water. “Steam was passed into cold water in a copper calorimeter until a suitable rise in temperature was obtained. Precautions were taken to ensure that the steam did not condense before it entered the calorimeter.” Draw a labelled diagram of the apparatus that might have been used in this experiment. (9) Give the equation used to calculate the specific latent heat of vaporization of water. (9) Describe how the mass of the steam passed into the water was determined. (6) State why it was necessary to ensure that the steam did not condense before it entered the calorimeter and explain how this was achieved. (12) Page 3 of 12 Fifth Year Physics Summer 2005 What is the advantage of having cold water in the calorimeter initially? (4) Question 3 In an experiment to verify the principle of conservation of momentum for a collision between two bodies, A and B, the following was recorded. Mass of A is o.2 Kg Mass of B is 0.4 Kg Before the collision, body A moves 0.45 m in 0.3 s. Before the collision, body B is at rest. After the collision, bodies A and B move 0.45 m in 0.9 s. Using the data, verify the principle of conservation of momentum. (12) Draw a labeled diagram of the apparatus used in the experiment. Page 4 of 12 (9) Fifth Year Physics Summer 2005 Explain how the time is measured accurately in this experiment. (6) Why is it important to minimize the effects of friction in this experiment and how is this achieved? (7) Give two other precautions that should be taken to ensure the accuracy of the values obtained. (6) Page 5 of 12 Fifth Year Physics Summer 2005 Question 4: Answer any EIGHT of the following parts (a), (b), (c) etc. (a) In Simple Harmonic Motion when is the velocity least? (7.5) Define the solar constant. (7.5) (b) (c) Write down the relationship between the linear velocity v and the angular velocity w for uniform circular motion. (7.5) Could a ‘thermos’ flask be used to keep a liquid cool on a warm day? Explain. (7.5) (d) (e) A spectrometer employs the phenomena of diffraction and interference to measure the wavelength of light. Explain the terms diffraction and interference. (7.5) Page 6 of 12 Fifth Year Physics Summer 2005 Write an expression to show the maximum order image which could be used. (7.5) (f) (g) Define U value? (7.5) (h) Two forces are applied to a body, as shown. What is the magnitude of the resultant force acting on the body? (7.5) i) A can of height 10 cm is submerged in water. What is the difference in pressure between the top and bottom of the can? (acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 ms-2 ; density of water = 1000 Kg m-3) (7.5) Page 7 of 12 Fifth Year Physics Summer 2005 j) Explain the term thermometric property. (7.5) Question 5 A. a) What is meant by centripetal force? b) In which direction does the centripetal force on a body act? c) Explain how a body acted upon by a centripetal force might nevertheless be moving with a constant speed. (6) (6) (8) a) b) c) A bicycle chain is wrapped around a front and rear sprocket. The radii of the front and rear sprockets are 10 cm and 4 cm respectively. The chain moves with a speed of 1.5ms-1 around the sprockets so that the bicycle moves at constant speed. Find the acceleration of a chain link i. in contact with the front sprocket ii. not in contact with a sprocket iii. in contact with the rear sprocket Page 8 of 12 (8) Fifth Year Physics Summer 2005 i) ii) iii) B. Explain the terms (i) refractive index (ii) total internal reflection. (8) Use a ray diagram to show that light can be reflected through 1800 by a triangular prism. (6) Page 9 of 12 Fifth Year Physics Summer 2005 Calculate the minimum value for the refractive index of the material of the prism for this to occur. (9) Draw the spectrometer (with labels) (9) Page 10 of 12 Fifth Year Physics Summer 2005 Question 6 A. Define (i) Work and (ii) Energy (6) Show that the loss in potential energy of a freely falling body is equal to the gain in its kinetic energy. (9) A girl swings back and forth on the end of a rope 8 m long that is attached to the ceiling of a gymnasium. If, at the highest point of each swing, she is 3 m from the ceiling, what is her maximum speed ? (12) B. Give an expression for Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation Page 11 of 12 (6) Fifth Year Physics Summer 2005 A satellite is in a circular orbit of Radius R around the earth, which has a mass M. Show that the period T of the satellite is given by T2 = 4π2R3 GM Where G is the universal constant of gravitation. (12) The first artificial satellite to orbit the earth, Sputnik, had a period of 96 minutes. What was its height above the surface of the earth, assuming that its orbit was circular? (15) (G = 6.67 * 10-11 N m2 Kg-2 ; M = 5.98 * 1024 Kg ; radius of the earth = 6.38 * 106 m) Page 12 of 12