* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mid-Ocean Ridges
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
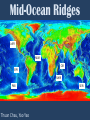
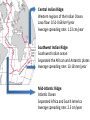
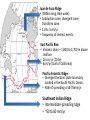
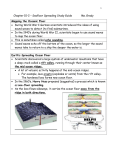
Mid-Ocean Ridges JdFR MAR EPR CIR SWIR PAR Thuan Chau, Yao Yao SEIR Mid-Ocean Ridge • Underwater mountain system formed by plate tectonics. • Oceanic spreading center – Valley of rifts running along its spine – Responsible for seafloor spreading • Magma, which comes out at the linear weakness part in the oceanic crust, becomes the new seafloor when it cools down. • Longest mountain range in the world 80,000km long (65,000km continuous). Classes of Ridges • Fast-spreading ridges, like the East Pacific Rise, the spreading rate is 100 to 200 millimeters per year. • Slow-spreading ridges, like the Mid Atlantic Ridge, the spreading rate is 20 to 40 millimeters per year. • Ultraslow-spreading ridges, like the Southwest Indian Ridge, the spreading rate is less than 20 millimeters per year. Central Indian Ridge: Western regions of the Indian Ocean. Lava flow: 0.51-0.68 km3/year Average spreading rate: 1.13 cm/year Southwest Indian Ridge: Southwest Indian ocean Separated the African and Antarctic plates Average spreading rate: 13-18 mm/year Mid-Atlantic Ridge: Atlantic Ocean Separated Africa and South America Average spreading rate: 2.5 cm/year Juan de Fuca Ridge: • (500km long, 8km wide) • Subduction zone, divergent zone, transform zone. • 1.8 to 3 cm/yr. • frequency of seismic events. East Pacific Rise: • Volcanic chain – 1,800 to 2,700 m above seafloor • 16 cm/ yr (Chile) • 6cm/yr (Gulf of California) Pacific Antarctic Ridge: • Divergent tectonic plate boundary located in the South Pacific Ocean. • Rate of spreading is 54-76mm/yr. Southeast Indian Ridge: • Intermediate spreading ridge • ~60 to 80 mm/yr