* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 1 - Mrs. Parsiola`s Homepage
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
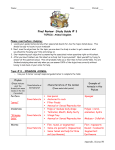
Life Science ____ Period Name: Date: Study Guide for Ch. 11 Animal Diversity Test Vocabulary: 1. Asymmetry: body organization that cannot be divided into mirror images 2. Bilateral symmetry: body organization that can be divided into two mirror images 3. Radial symmetry: body organization that can be divided into multiple mirror images anywhere through the central axis 4. Invertebrate: animal that does not have a backbone 5. Vertebrate: animal that does have a backbone 6. Appendage: structure that extends from the central part of the body, like an arm or leg 7. Exoskeleton: thick, hard outer covering that protects and supports animals’ bodies 8. Notochord: flexible, rod-shaped structure that supports the body of a developing chordate Lesson 1: What defines an Animal? 1. What series of characteristics do all animals share? a. Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. b. They have specialized cells for different functions (ex. digestion, reproduction, vision, or taste). c. Animals have collagen (protein that surrounds cells to help keep their shape). d. They get energy by eating other organisms. e. Animals digest their food. Unit 7 Astronomy Ch.22-25 - Space (pp. 636-767) 1 Life Science ____ Period Name: Date: 2. How can animals be classified? a. They can be classified into two large categories: Invertebrates or Vertebrates. b. They can be classified by their symmetry: asymmetrical, radial, or bilateral. c. They can be classified by their molecular classification (DNA, RNA). 3. Animal Classification Concept Map Organisms in Kingdom Animalia can be classified into nine (9) major phyla according to these characteristics backbone vertebrates DNA invertebrates symmetry asymmetry bilateral radial Unit 7 Astronomy Ch.22-25 - Space (pp. 636-767) 2 Life Science ____ Period Name: Date: PORIFERA (sponges) CNIDARIA (jellyfish, sea anemone) PLATYHELMINTHES (flatworms) NEMATODA (roundworms) ANNELIDA (segmented worms-earthworm, leech) MOLLUSCA (snail, slug, clam, squid, octopus) ECHINODERMATA (starfish, sea cucumber, sea urchin) ARTHROPODA (insect, shrimp, crab, spider) CHORDATA (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals) Unit 7 Astronomy Ch.22-25 - Space (pp. 636-767) 3 Life Science ____ Period Name: Date: Lesson 2: Invertebrate Phyla 1. What are the characteristics of invertebrates? a. no internal support structure b. smaller than and slower than vertebrates c. diverse body plans and physical characteristics 2. Invertebrates include 95-99 percent of all animal species. Arthropods contain the most animals of the 8 invertebrate phyla. The largest order of Arthropods is the insects. 3. Know the characteristics and symmetry for the 8 invertebrate phyla: Lesson 3: Phylum Chordata 1. What are the characteristics of Chordates? (Some only appear during embryonic stages). a. has notochord (flexible, rod-shaped structure that supports the body) b. a nerve cord (central nervous system) c. a tail d. pharyngeal pouches Unit 7 Astronomy Ch.22-25 - Space (pp. 636-767) 4 Life Science ____ Period Name: Date: 2. What are the characteristics of a vertebrate? a. all have a backbone that surrounds a spinal cord (spinal column or spine) b. all have a digestive system with two openings, circulatory system to move blood, and nervous system including brain 3. Most chordates are vertebrates with the exception of two invertebrates: tunicates and lancelets (which have a notochord). 4. The classes of vertebrates differ based on presence or absence of characteristics such as gills, fins, scales, legs, wings, fur, and eggs. 5. Know the characteristics and examples of the classes of vertebrates: FISH Characteristic: two chambered heart; gills to absorb oxygen gas from water; paired fins Jawless fish Cartilaginous fish Boney fish AMPHIBIA Characteristic: three chambered heart; live part of life in water (gills) and part on land (lungs); eggs without hard protective covers; smooth moist skin Frog Salamander Unit 7 Astronomy Ch.22-25 - Space (pp. 636-767) 5 Toad Life Science ____ Period Name: Date: REPTILIA Characteristic: three chambered heart; lungs; eggs with leathery shell; scales and waterproof skin Lizard Snake Turtle Alligator AVES Characteristic: four chambered heart; hollow bones; eggs with hard shell; feathers; beak, no teeth, gizzard to grind food MAMMALIA Characteristic: four chambered heart; hair or fur; live young (except platypus – eggs); mammary glands that produce milk INCLUDES HUMANS Unit 7 Astronomy Ch.22-25 - Space (pp. 636-767) 6