* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Membranes Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
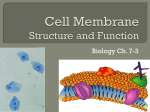
Cell Membranes Study Guide Name Per. 1. The function of the cell membrane is to 2. Draw and label a cell membrane using the following terms: phospholipid bilayer, transport protein, cholesterol, carbohydrate chain. 3. _____________________ Transport: does not require ATP a. molecules travel ____________ the concentration gradient ( from _________ _________ ) Types Structure Traveled Through Molecule Size Molecules Involved b. c. d. 4. Osmosis: diffusion of _________________ Solute Concentration Higher in the Where does the water move? What happens to the size of the cell? Drawing 5. Hypertonic Solution 6. Hypotonic Solution 7. Isotonic Solution 8. ___________________ Transport: requires ATP Structure Direction of Concentration Types Used Movement Gradient a. Size & Examples of molecules b. c. 9. Why is a concentration gradient important in biology? 10. Molecules diffuse because 11. When molecules diffuse, the goal is to reach . , when solution is . Cell Membrane Concept Map active transport ATP bacteria Name cell membrane diffusion endocytosis exocytosis facilitated diffusion food for unicellular ions lipid secretions monomers Period osmosis passive transport phospholipid bilayer protein secretions transport protein x2 wastes Exchange of molecules through the 1. Against the concentration gradient (low to high) Down the concentration gradient (high to low) 2. 10. large molecules transported by small & medium molecules requires pushed by transported through the 3. 6. 7. 11. of water 4. in out small molecules move through medium molecules move through examples 5. * 8. * 9. * * * 12. 13. * * also called 16. 15.