* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name: Date: Mr. Art Period: Solving Linear Equations, Linear
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Unification (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Exact solutions in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
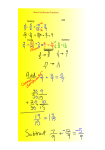
Name: ______________________________ Mr. Art Date: _______________ Period: ______________ Solving Linear Equations, Linear Systems Algebraically I. Solving Linear Equations Steps: * Only do steps 1, 2, or 3 if possible, if not start at step 4! 1) “Clear” Parentheses (by Distributing when necessary) Multiply the term on outside of the 2) Combine Like Terms Add or Subtract terms that have the same variable AND the same exponent 3) Variables on Both Sides of the Equal Sign “Undo” smaller term with variable on one side of the equal sign from the larger term with variable on the other side of the equal sign. By the Inverse (opposite) Addition or Subtraction 4) “Undo” the Constant By the Inverse (opposite) Addition or Subtraction Constant number alone (stays the same) 5) “Undo” the Coefficient By the Inverse (opposite) Division or Multiplication Coefficient number with variable 6) Check (your solution) 1) Rewrite 2) Replace 3) Recalculate No Distributing, Combining Like Terms, or Inverse operations in Check. Simply plug in value to determine if both sides of the equation are equal. Reminder: Negative (-) is the same as Subtraction (-) Positive (+) is the same as Addition (+) Ex. 5 – x = 12 is the same as – x + 5 = 12 Ex. 5 + x = 12 is the same as x + 5 = 12 An equation is like a scale…whatever you do to one side, must also be done to the other side 1 II. Literal Equations: equations with multiple variables *Solve 10 = 2x + 4 to help you with the steps. II. Systems Algebraically 1) Elimination Method: Steps: 1) Eliminate one of the variables ( same sign = subtract, different signs = add) 2) Solve for the variable you didn't eliminate 3) Plug the variable you just solved for back into one of the equations to find the other. a) b) 2 c) Each cookie costs $0.60 or 60 cents 2) Substitution Method Steps: 1) When one of the equations is equal to one of the variables (like how the example below has an equation already equal to x), 2) Plug in what is equal to that variable (4y) into the other equation in place of that original variable (4y will replace x in the 5x - 3y = 17 equation). 3) The result will be that one variable will be eliminated and you will solve for the other. 4) Once you solve for the first variable, plug the answer into one of the two equations then solve for the second variable. a) b) 3