* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproduction in plants
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
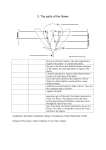
Reproduction in plants Instructional Objectives: -Students will be able to recall terms like unisexual, besaxual, pollination. - Students will be able to recognize the different parts of a flower. -Students will be able to differentiate between asexual and sexual reproduction. - Students will be able to cite illustrations of bisexual flowers. - students will be able to sketch and label the different parts of a flower. Concepts: -Flowering and non-flowering plants. -flowers are reproductive parts of a plant. -In sexual reproduction there is involvement of male and female gamete. -Unisexual flowers have only one type of gamete in them. -Bisexual flowers have both gametes in the same flower. -Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of a flower is called pollination. Previous Knowledge: -Have knowledge about different types of flowers. -parts of a flower -Seeds are required to grow a new plant. Instructional Materials: Valvet paper and flannel board, worksheets, C.B. Set Induction: Activity -1 Put a tick mark at appropriate places. PLANTS WITH FLOWERS WITHOUT FLOWERS Rose Ginger Bryophyllum Hibiscus Mango Cashew Potato Spirogyra Tr. Discusses worksheet with the students. Plants that produce flowers are called as flowering plants and plants that do not produce flowers are called as non-flowering plants. Most of the flowering plants require seeds to give rise to a new plant. Statement of the topic: So in today’s class we shall see how flowering plants reproduce in the chapter “Reproduction in flowering plants”. Development of the topic: Activity - 1 Parts of a flower: The flower contains the reproductive parts or the gametes. Therefore the flower is said to be the reproductive part of the plant. The stamen is the male reproductive part and is made up of 2 parts: anther and filament. Anther contains pollen grains which is the male gamete of the flower. Pistil is the female reproductive part of the plant. The pistil is made up of three parts: stigma, style and ovary. Ovary contains ovules which are the female gametes of a flower. The type of reproduction in which the male and female gamete fuse to form the fruit and give rise to a new plant is called as sexual reproduction. Some plants produce flowers having only one gamete (either male or female gamete). Flowers which contain either only the pistil or only the stamen are called unisexual flowers. Eg. Flowers of papaya plant. A flower which contains both stamens and style is called bisexual flower. In sexual reproduction male and female gametes fuse to form the zygote which further grows and forms new plant. The pollens first come in contact with the stigma. The transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of a flower is called pollination. Evaluation: Homework: Draw a picture of the flower and label its parts