* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 54: Community Ecology (with answers)
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
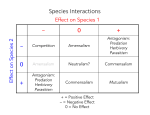
Chapter 54: Community Ecology Week 15, Session 1 Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Kelsey Bio 211 (5) Dr. Holscher 12-7-09 1. What is a community? a group of populations of different species living close enough to interact 2. Fill in the table of intraspecific interactions: Competition +/-, +/+, -/-, or +/0 -/- Description Individuals of different species compete for resources One species benefits, the other suffers Predation +/- Herbivory +/- Organism eats a plant Parasitism +/- A parasite benefits, the host is harmed Disease +/- Mostly affects communities Mutualism +/+ Both individuals benefit Commensalism +/0 One individual benefits, the other is neither helped nor harmed 3. What does the competitive exclusion principle state? When two species are competing for the same resource in the same community, only one can survive (unless resource partitioning is used). 4. What does the ecological niche concept state? When two species have the exact same ecological niche, only one species can survive in that environment. Supplemental Instruction 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 294-6624 www.si.iastate.edu 5. __Resource partitioning___________________ makes it possible for similar species to coexist in the same community. 6. ___Aposematic________________ coloration warns predators to stay away. 7. What is the difference between Batesian and Mullerian mimicry? Batesian: a non-harmful individual mimics a harmful individual, Mullerian: two harmful individuals mimic one another 8. How is parasitoidism different than parasitism? In parasitoidism, the host dies (in parasitism, the parasite wants the host to stay alive). 9. Species richness refers to… the number of different species 10. Relative abundance refers to… the number of individuals of each species present 11. True or false: Two communities that have the same richness must have the same abundance. FALSE 12. Fill in the trophic levels from producers to consumers: Left to right: primary producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, tertiary consumer, quaternary consumer 13. Briefly explain the two competing hypotheses of food chain length: a. inefficiency of energy transfer limits length b. dynamic stability hypothesis: longer food chains are less stable 14. What is the maximum number of links a food chain can typically have? 5 15. What is a dominant species? most abundant or consisting of greatest biomass 16. What is a keystone species? a species that has a strong central role or niche (ex. otters, urchins, kelp, whales) 17. What is a foundation species? a species that physically alters the environment, “engineers” (ex. beaver) 18. What does the nonequilibrium model of communities state? Species are never at equilibrium; they are always dealing with disturbances. 19. What is the difference between primary and secondary succession? primary: no soil existed before the disturbance, secondary: soil existed before the disturbance 20. What two biogeographic factors contribute to biodiversity? solar energy and area