* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gravity - Model High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
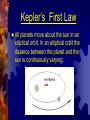
Gravity and the Laws of Motion Mass Mass is the amount of “stuff” (matter) in an object. Measured in grams (kg, mg, cg, etc.) Mass will not change unless matter is added or taken away. Weight Weight is the gravitational force exerted on an object by Earth (or the moon, Jupiter, Sun, etc.) It is a FORCE so it’s measured in Newtons (N). Weight can change depending on where you are located. Galileo Galilei 1564-1642 Italian astronomer and physicist First true “Experimentalist”. Set forth the basic ideas of Motion. All objects fall at the same rate. (heavy or light!) Sir Issac Newton 1643-1727 English mathematician and physicist Laws of MOTION Quick Review of Newton’s discoveries… Laws 1st Law – The Law of Inertia 2nd Law – acceleration = Force mass 3rd Law – Forces occur in action-reaction pairs Acceleration due to gravity, g All objects regardless of their mass are accelerated equally by gravity Since this acceleration is so important to the motion of all objects on the surface of the earth it is assigned g = 9.8 m/s2 (or 10 m/s2) What is gravity? Gravity – the force that pulls objects toward the earth. Gravity Continued… Freefall - An object accelerates as it falls. Near the earth objects fall at the same rate regardless of their mass. g = 9.8 m/s2 Gravity continued… Law of Universal Gravitation This law states that the force of Gravity acts between all objects in the universe. Newton & Gravity Isaac Newton was the first to deduce that the force that makes an apple fall is the same force that keeps the moon in its orbit. But then he asked himself… Does the falling apple exert a force on the earth? Why doesn’t the moon fall into the earth? Gravity . . . The apple DOES exert a force on the Earth! Does The the Earth notice? Why? moon IS falling! HUH?!? Satellite Motion! Newtonian Mountain Space Dangers The Story of 9.8… From before we know that a 1 kg mass exerts a force of 9.8 N on the Earth because… Fweight = mass x gravity Fw = (1kg)(9.8 m/s2) Fw = 9.8 N Where did this “9.8” come from in the first place? The Story of 9.8… 1 kg mass distance = radius Earth mobject mEarth m1m2 F G 2 becomes... F G d rEarth 2 F 6.67 10 F = 9.8 N 11 N m / kg 2 2 1kg 5.97 x 1024 kg 2 6.38 x 106 m Acceleration due to Gravity at Different Places on Earth… g varies slightly due to differences in the distance from the center of the earth (altitude or latitude) North Pole Panama Canal New York City Denver g = 9.832 m/s2 g = 9.782 m/s2 g = 9.803 m/s2 g = 9.796 m/s2 Acceleration due to gravity on Different Planets… These depend on the planet’s mass and radius. Jupiter Neptune Saturn Uranus Earth Venus Mercury Mars Pluto Moon 2.54 x g 1.20 x g 1.06 x g 0.92 x g 1.00 0.92 x g 0.38 x g 0.38 x g uncertain 0.16 x g Acceleration due to gravity depends on the planet’s mass and radius. Acceleration due to gravity depends on the planet’s mass and radius. Acceleration due to gravity depends on the planet’s mass and radius. Guess your weight on Mars! This website will tell you how much you would weigh if you were on any of the other planets. http://www.exploratorium.edu/ronh/w eight/index.html Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation Depends Mass of the two attracting objects (m1 & m2) Directly proportional Distance between the two objects (d) on… Inversely proportional Universal Gravitation Constant (G) G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2 Ya’ Gotta Obey the Law! Who are you attracted to?? Maybe not Romantically by definitely Gravitationally! Two bodies are attracted to each other due to their mass and the distance between them. Why don’t we always feel a gravitational attraction? In order for a gravitational attraction to be felt the mass of one of the bodies must be very large. The earth is many times more massive than you are. You can sense the Force of Attraction. Kepler’s First Law All planets move about the sun in an elliptical orbit. In an elliptical orbit the distance between the planet and the sun is continuously varying: Why do we have seasons? Are we closer to the sun in summer? And farther away in the winter? What does the earth’s revolution around the sun cause? The earth is tilted on its axis 23.5 degrees. to the plane of the earth’s orbit around the sun Seasons Mid-latitudes enjoy a change of seasons. Earth Revolution APHELION / PERIHELION “Helios” - Greek word for sun Prefix “Ap” means farthest Prefix “Peri” means closest Which way did it go? Better watch out for the cops!